Insights
As Taiwan’s leading lock designer and manufacturer, SINOX Co., Ltd. continues to broaden its product portfolio, delivering comprehensive security solutions for office equipment, outdoor recreation, travel luggage, and electronic security applications.
2025-08-26 08:41:17
The global plastic blow molding machine market is rapidly upgrading, shifting from mere shaping to full-scale efficiency, energy savings, and smart manufacturing. Stricter regulations, rising energy costs, and growing ESG pressures are driving machines to evolve into intelligent systems with remote monitoring, energy management, and advanced automation. With its “chocolate-grade” customization, all-electric energy-efficient designs, and continuous R&D innovation, Chia Ming helps customers adapt quickly to market changes, cut operating costs, and boost competitiveness—making the company not just an equipment supplier, but a key partner in advancing the industry toward a smarter, more sustainable future.
2025-08-26 08:54:08
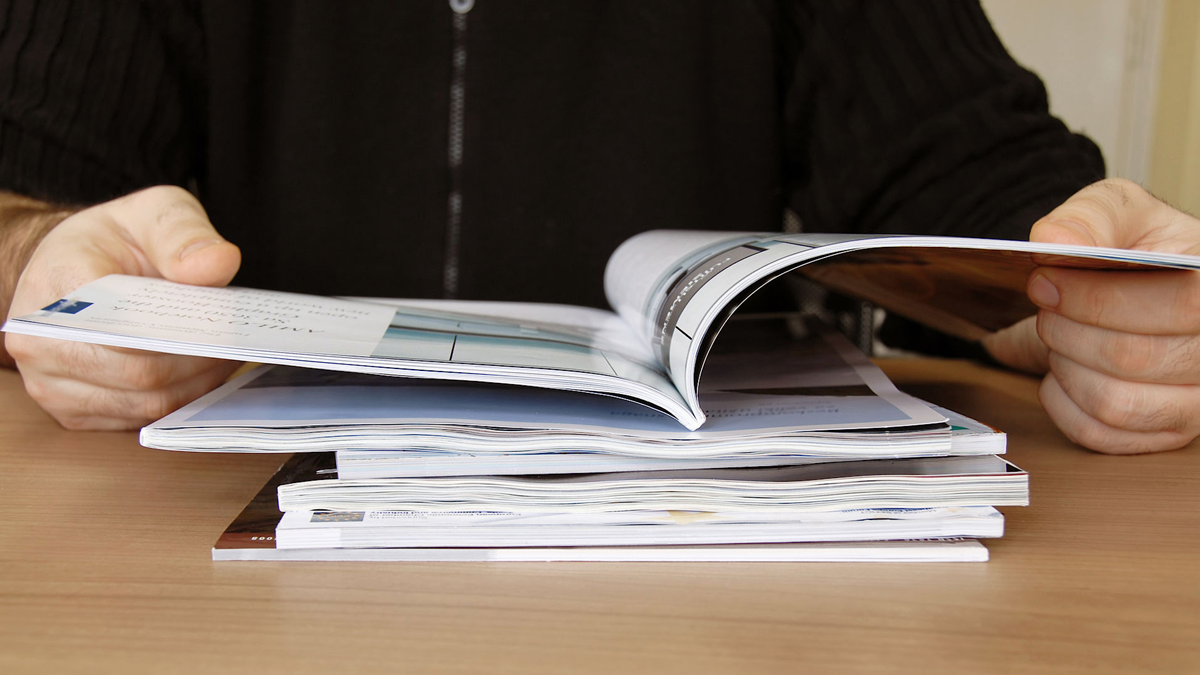
Driven by the wave of digitalization, we have long grown accustomed to a daily life where information constantly “scrolls” into our view. E-books, online news platforms, and short videos occupy our fragmented time, while print publications were once seen as relics destined to fade away. Yet history is often full of reversals—just as digital media reached its peak in speed and density, print quietly returned to the stage, even becoming an “irreplaceable choice” for certain audiences. This phenomenon not only challenges our linear imagination of media evolution but also reveals deeper psychological needs behind human reading behaviors.
2025-08-26 08:32:29
In the modern manufacturing era, where lightweight design and high performance are the top priorities, aluminum alloy forging has become one of the core processes across multiple industries. Whether in automotive, motorcycles, bicycles, aerospace, or industrial equipment, forged aluminum components are widely adopted due to their unique combination of light weight and high strength. For manufacturers, forging is not merely a processing method—it is a solution that ensures quality, efficiency, and reliability. Through precise material selection, professional process planning, and stringent quality control, companies can deliver high-performance products that meet international standards.
2025-08-25 17:03:41
JuPu Light Technology Limited, a company dedicated to innovation in far-infrared medical devices, is once again setting new trends in photonic medicine with its proprietary Photon Energy Wave (PEW) technology.
2025-08-25 16:30:14
Soft polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) waste are widely used in modern plastic industries, including packaging films, agricultural coverings, garbage bags, and logistics materials. Due to their high usage volume and recycling challenges, the effective recovery and processing of these materials have become a critical aspect of sustainable plastic management.
2025-08-25 15:59:12
Since its establishment in 1988, Matila Industrial Co., Ltd. has been a leading force in the plastic machinery sector for more than three decades. With outstanding technology and innovative designs, the company has become a highly respected Taiwanese brand in international markets. To date, Matila’s products have been successfully exported to over 50 countries across Europe, Asia, Latin America, and Africa, earning the trust and support of clients worldwide.
2025-08-25 15:26:05
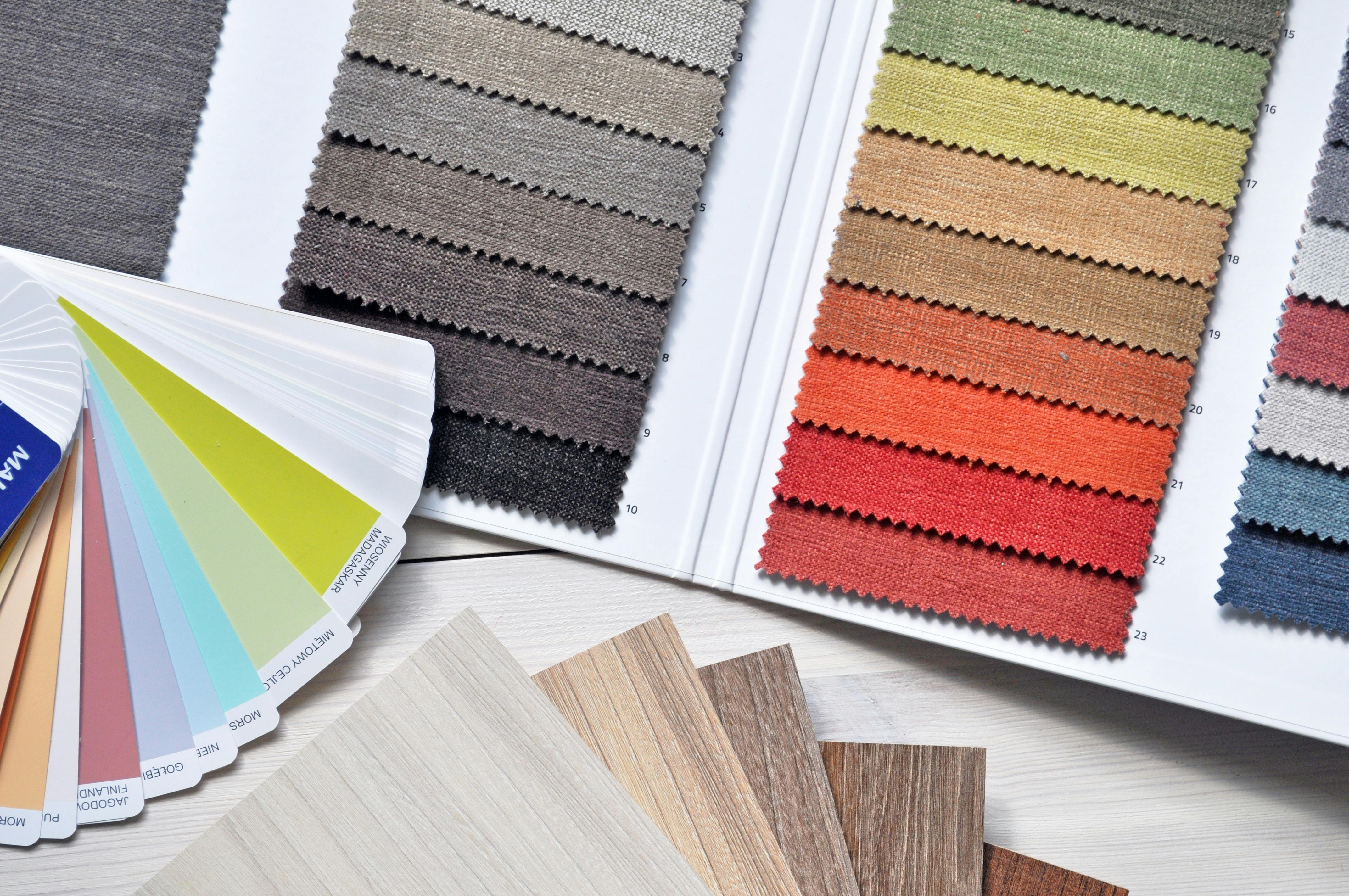
The global textile industry is riding the dual wave of sustainable transformation and diversified market demands. Brands are increasingly seeking high-performance fabrics while placing great emphasis on eco-friendly manufacturing processes and product differentiation. Yichun Textile Co., Ltd., founded in 1988, leverages its more than thirty years of rich professional experience to combine green innovation and customized manufacturing as its two core strengths. The company is fully committed to providing global clients with textile solutions that offer exceptional functionality, sustainable value, and market competitiveness.
2025-08-25 14:28:35
Since its establishment in 1996 in the Shengang District Textile Industrial Park of Taichung, Wei-Syun Industrial Co., Ltd. has been committed to innovation and sustainable practices in circular knitted fabrics. Guided by its core principles of integrity, precision, sustainability, and leadership, the company continuously adopts new technologies and advanced materials to meet evolving market trends and customer needs, while actively expanding into international markets to serve a global clientele.
2025-08-25 12:02:31
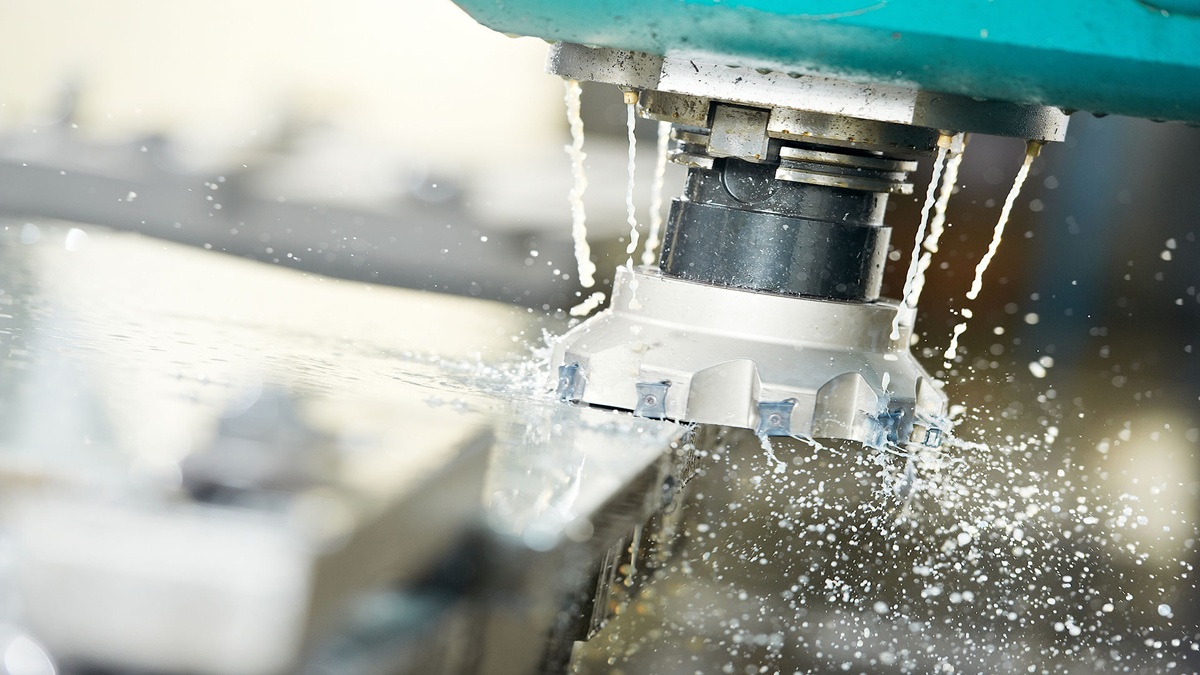
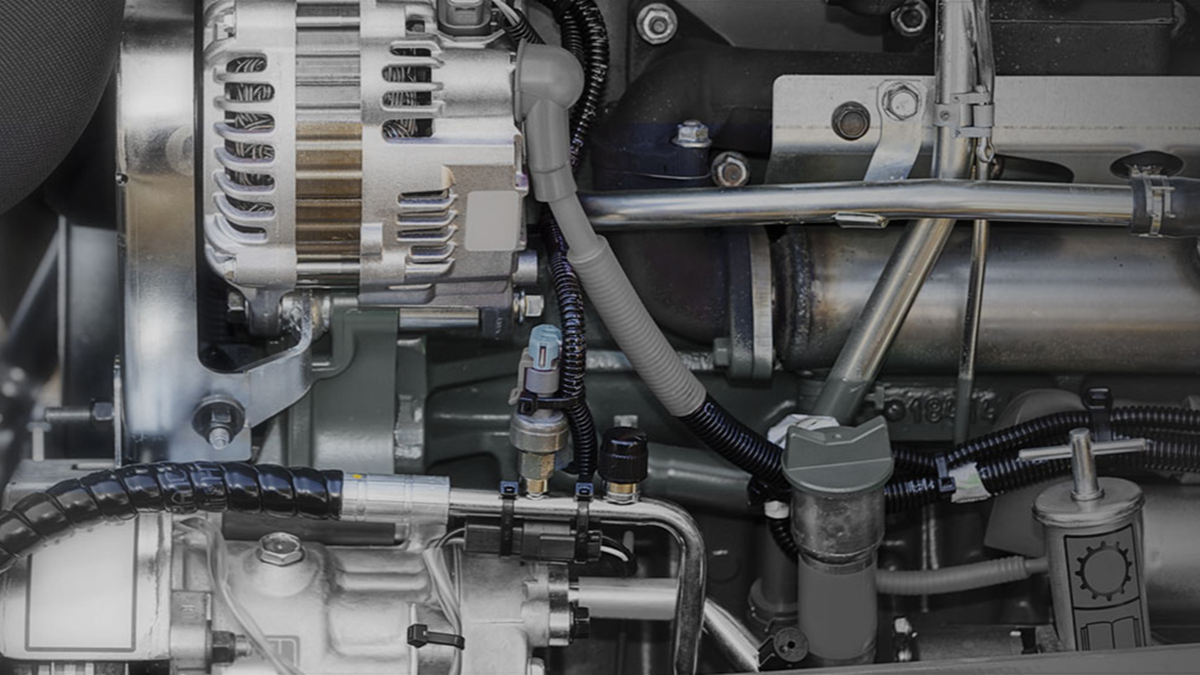
Machine tools are the cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling precise cutting, forming, and machining of metals and other materials. During operation, these machines generate significant friction and cutting heat, which, without proper management, can lead to tool wear, workpiece deformation, and reduced machining accuracy. Lubrication and cooling systems are essential for mitigating these issues, with lubrication reducing friction and wear, and cooling dissipating heat to maintain thermal stability. Together, these systems enhance machining efficiency, extend equipment lifespan, and improve surface quality. Research indicates that effective lubrication and cooling can boost machining performance by up to 30%. This article explores the critical components—lubrication pumps, pipes, coolant pumps, and filters—while highlighting advanced techniques and future trends.
2025-08-22 16:56:48
Hot Topic
Agree


.jpg)