As adoption of 3D printing spreads throughout the larger sector of industrial manufacturing, the value of the technology as more than just a rapid prototyping tool is becoming increasingly evident. In this article, we gave an overview of how 3D printing is used to fabricate molds and dies for injection molding and die casting.
3D Printed Molds
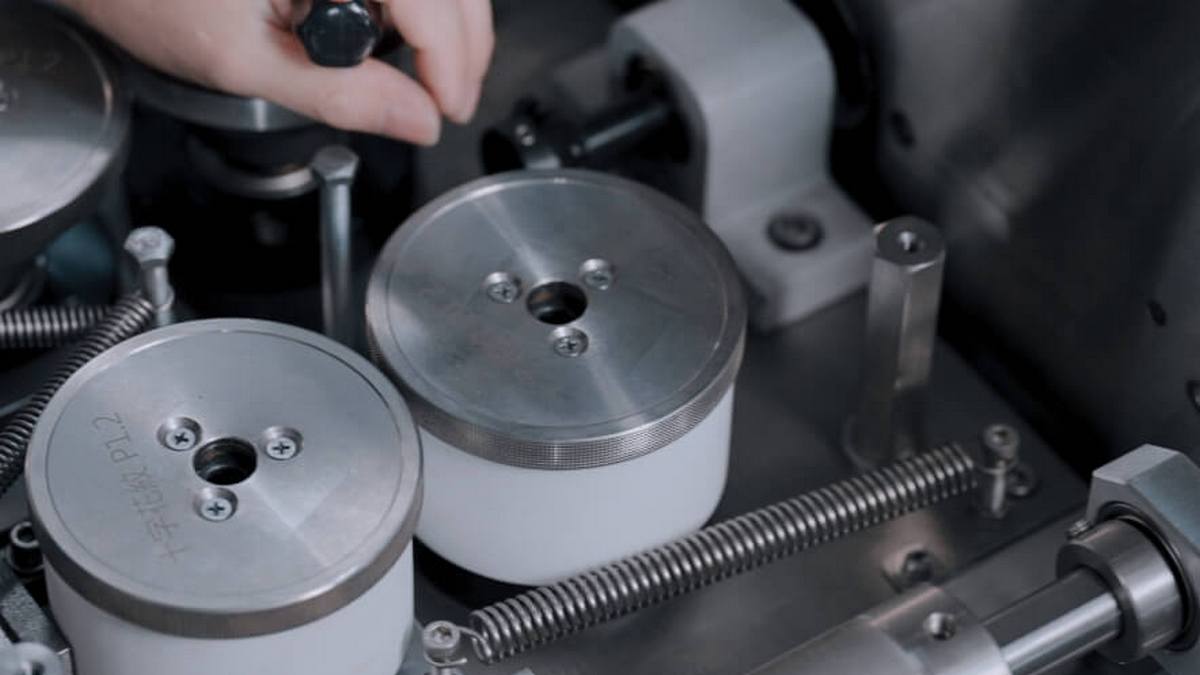
The most common for mass manufacturing plastic parts, injection molding involves injecting liquid plastic into a mold at high pressure. Filling all of the cavities of the mold, the plastic hardens, and the finished part is removed. Most often, the polymers used are thermoplastics, which are melted at high temperatures and cool upon entering the mold. Typically, molds are precision-machined from aluminum or steel, which can cost from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars. Therefore, injection molding is most cost-effective at high volumes in making tens of thousands to millions of parts. For low-run injection molding of 50 to 100 parts, 3D printing can be a more cost-effective option. Even when additive manufacturing (AM) isn’t being used to produce end parts, businesses are learning that it can be used for the fabrication of tooling for their traditional production processes. In particular, 3D printing molds and dies for injection molding and die casting holds a lot of potential due to the various benefits that AM offers in terms of making custom, on-demand and complex parts.
In particular, additive manufacturing (AM) can be more cost-effective for small batches of parts; however, in some cases, the technology can provide some benefits that are unique to 3D printing, regardless of batch size. This is particularly true of 3D-printed metal molds and dies that can survive much longer than plastic molds discussed in part one.
In many instances, however, different technologies are used for different stages of manufacturing. 3D printing, for example, is frequently preferred for prototyping, since it is simple, transportable and comes with incredibly low start-up costs. Injection molding, meanwhile, is often the go-to process for huge volumes of end-use parts, since it is fast and highly repeatable. One technology serves the research and development phase; the other takes care of production.
There are numerous examples where 3D-printed molds have improved the injection molding process in the following. Tool manufacturer cut cycle time by 17 percent, ultimately also reducing production time to market from 18 to 13 days. Polish tooling and injection molding company reduced cycle times by 30 percent, even was able to reduce the temperature of its tooling by 20°C, resulting in a 20-second drop in cooling times. Another tool center was able to cut its cycle time by 60 percent and scrap rate from 50 percent to zero.
Things Need to Consider if Moving from 3D Printing to Injection Molding
What happens when you create a 3D printed prototype and need to move to production with injection molding? How can you ensure a molded part will match the specifications of its printed counterpart, given the radical differences in the two manufacturing technologies? How do you plan to ensure success in both prototyping and production?
Design for injection molding where possible
If you’re planning to eventually move from 3D printing to injection molding, 3D printed prototypes must be designed so they are not only printable but also moldable. And this means following injection molding design principles — even during the 3D printing stage. Draft angles should be included, overhangs should be avoided and sharp corners should be rounded. Furthermore, complex infill patterns (which would improve the strength and efficiency of the 3D printed part) should be abandoned in favor of simple ribs, since mold cannot replicate those complex infill patterns.
Print with production materials
Injection molding, a highly flexible process, is compatible with a huge variety of plastics, while 3D printing is more limited in terms of available materials. But when designing a 3D printed prototype, it is important to choose a material that matches or at least mimics the material to be used during production.
Polish prototypes for a ‘molded’ finish
For mechanical or aesthetic parts, it is important to create prototypes with a surface finish that represents the finish of the final part. Mechanical parts may demand a certain level of friction or smoothness, so a prototype with a radically different texture will not be particularly useful. Thankfully, surface finishing treatments can be applied to transform the exterior of a 3D printed prototype. With a professional polish, applied with a cloth or buffing wheel, the surface roughness of a printed part can be dramatically reduced, even producing a mirror-like shine.
Go beyond FDM
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printers are a hugely popular choice for prototyping. They’re cheap, easy-to-use and compatible with a huge range of plastic filaments. On the other hand, more high-quality alternatives to FDM are capable of producing a more molded-like part.
Seek specialist advice
It may seem obvious, but one of the easiest ways to ensure a smooth transition between 3D printed prototypes and injection molded final parts is to discuss the entire project with an expert. If you plan to order a prototype through a professional service provider, be sure to let them know that the end-use part will be made using injection molding. Better still, use the same service provider for prototyping and production, allowing them to bridge the two processes with their expert know-how.
Now you have already known about 3D printing used in the die and mold industry, and we also give five things that you need to consider when you are moving from 3D printed to injection molding. I think it is not difficult to understand 3D printing knowledge, but it harder is to use it in real. However, you do not worry about that, because we will offer the latest news every day, just lock on our website.









.jpg)



