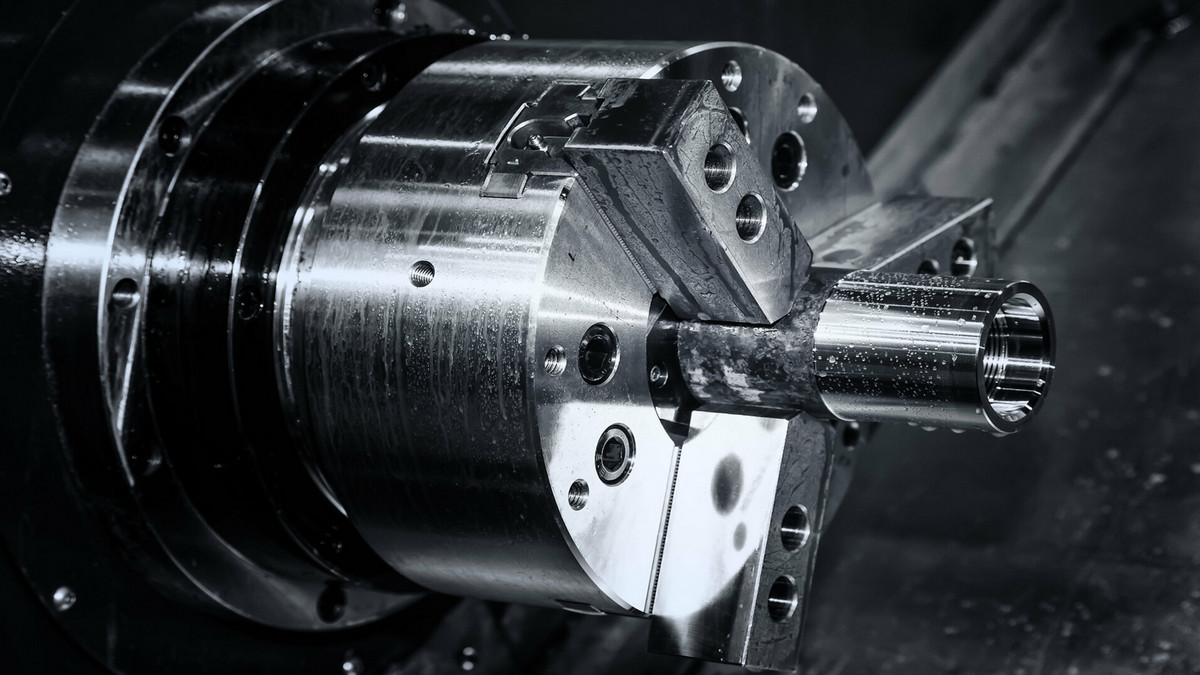
Collet is a cylindrical fixture used to install a drill bit or a milling cutter on a milling machine. It is a fixing device used to fix and reinforce parts that need to be modified.
What is a Chuck?
Chuck is the device responsible for clamping the workpiece on the machine tool and can be divided into power chuck and manual chuck according to the type. Collets typically use jaws to grip a tool or workpiece, usually arranged in a radially symmetrical fashion. Chucks on some lathes have independently moving jaws that allow them to grip irregularly shaped objects. More complex designs will have specially shaped jaws, higher numbers of jaws, quick-release mechanisms, etc. Instead of jaws, collets can use magnets, vacuum, or collets, which are flexible collars or sleeves.
The double-top clamping method is suitable for parts that are longer or have more processing procedures, and are generally used for finishing. The power chuck is mainly driven by hydraulic pressure and has a high clamping force. It is widely used on machine tools and is called a hydraulic chuck. When the workpiece is easily deformed, it will choose the pneumatic drive type to reduce the clamping force, which is called air pressure. Chuck, or another precision pneumatic chuck. The manual chuck is used by traditional high-speed lathes. It uses manpower to tighten the jaws to hold the workpiece, and it does not need a power source.
- Insufficient clamping force of the collet: During processing, the workpiece will be displaced due to high-speed rotation, and the turning tool will have strong pressure to squeeze the workpiece during processing, and the machining reference point will therefore be unstable.
- The clamping force of the collet is too large: During processing, the workpiece will be imprinted with excessive processing force, which will cause the workpiece to be pinched by the jaws and cause damage to the finished product.
What is the Structural Principle of the Chuck?
CNC milling machine chuck is a kind of cylindrical fixture used to install on the milling machine to confine the drill bit or milling cutter. It is a fixing device used to fix and strengthen parts that need to be modified.
The structural principle is to put the collet into the lock nut, and then gently screw the lock nut with the spring collet on the tool handle, post, or spindle. Be sure to clean the threaded part, positioning surface, and cone surface of the collet and lock nut. During the installation process of the collet and the lock nut, the collet and the lock nut must be inclined at a certain angle, and then gently put into the lock slot of the lock nut.
What are the Functions of the Chuck?
- Control the movement of machinery, such as valve springs in internal combustion engines, control springs in clutches, etc.
- Absorb vibration and impact energy, such as buffer springs under automobiles and train carriages, vibration-absorbing springs in couplings, etc.
- Store and output energy as power, such as clock springs, springs in firearms, etc.
- Used as force-measuring components, such as force-measuring devices, springs in spring scales, etc. The ratio of load to deflection of a spring is the spring rate, and the greater the rate, the stiffer the spring.
What are the Classifications of Chucks?
According to the number of chuck claws, it can be divided into:
- Two-jaw chuck
- Three-jaw chuck: The three-jaw chuck is the most widely used universal fixture on lathes. It can be centered automatically, but the clamping force is small and the accuracy is average, about 0.05-0.15mm.
- Four-jaw chuck: If a larger clamping force is required, a four-jaw chuck can be used. Since the four jaws can move independently, the four-jaw chuck can install workpieces with irregular cross-sections such as ellipses, squares, and rectangles. At the same time, the clamping force of the four-jaw chuck is larger than that of the three-jaw chuck, so it is often used to install larger round workpieces.
- Six-jaw chuck
- Special chuck
Power can be divided into:
- Single-action chuck: Usually a four-jaw chuck, each jaw moves independently, suitable for irregular work objects.
- Linked chuck: Usually a three-jaw chuck, the three jaws move at the same time, suitable for regular work objects.
- Dual-purpose chucks: Can move independently or at the same time.
- Electromagnetic Chuck: There are no claws on the chuck, and the workpiece is attached to the chuck using an electromagnet.
- Hydraulic chuck: Chuck drove by hydraulic pressure.
- Electric chuck: A chuck driven by an electric motor.
- Mechanical chuck
The structure can also be divided into:
What is a Fully Sealed Power Chuck?
The main feature of the fully sealed power chuck is the fully sealed design, which can prevent the internal lubricating grease from being washed away by the cutting water and gradually losing the clamping force, and extend the maintenance interval of the chuck. Compared with the traditional power chuck, the lubrication interval can be extended by about 30-90 times depending on the processing conditions. It can effectively reduce the daily lubrication frequency of processing workers and the cumbersome maintenance and disassembly, and improve production efficiency. The full sealing function can also prevent chips or cutting powder from entering the main body of the chuck, reduce wear and keep the chuck in a high-precision state for a long time. In addition, the amount of lubricating grease is reduced, and the pollution of the lubricating grease to the cutting fluid is reduced, which is also beneficial to the environment.
The recommended application range of fully sealed collets includes unmanned operations, dry processing of castings and forgings, processing under high-pressure coolant, and vertical lathes. Given the above characteristics, the long-term stable clamping force and clamping accuracy of the fully sealed chuck can reduce the maintenance frequency and the amount of lubricating grease and can be equipped with central water injection or air injection according to the needs of automated production. It will be the driving force in the future. Important development trends of collets.
How to Choose the Chuck?
There are several factors to consider when deciding which fixture will work better. For a given lathe machining task, when deciding whether to choose a collet or a jaw chuck, all of the following factors need to be considered. Spindle Load Capacity The maximum allowable weight of a lathe spindle is based on the bearing load capacity, and if the combined weight of the chuck and workpiece is too high, the bearings may be overloaded. For those processing tasks where there is a risk of exceeding the limit, this risk may determine people's choice of work-holding fixtures. Jaw chucks are often heavier than equivalent spring chucks. Therefore, where weight control is required, spring clamps are preferred. Head is the appropriate choice. Batch sizes Both large and small batches are suitable for collet chucks.
- In the processing of small batches and multiple tasks, the advantages of spring collets are related to the product changeover time. It takes about 15 to 20 minutes to replace the jaws of standard jaw chucks, and 1 minute for quick-change jaw chucks. The collet replacement of the quick-change collet only takes 15 to 20 seconds. When the product changes frequently, the time saved is considerable.
- The time savings related to clamping can be accumulated when processing large batches. Collet chucks require less opening and closing time than jaw chucks, by reducing non-cutting time for changing from one workpiece to the next, to reduce processing cycle time.
Spindle-speed collets tend to be a better choice for turning at very high spindle speeds for two main reasons:
- One reason has to do with the quality of the chuck, assuming the same spindle horsepower is driving the jaw chuck and collet, thicker jaw chucks take longer to accelerate to the required speed, and longer acceleration times will be extended the duty cycle, reducing productivity.
- Another reason has to do with centrifugal force, since it increases as the square of the rpm increases, so, in the case of high-speed cutting, this value is important. For example, doubling the spindle speed will quadruple the centrifugal force. This force pulls the chuck jaws off center, tending to reduce clamping force. But with collets, centrifugal force does not have a noticeable effect. Thus, the clamping force will be more stable over the entire processing speed range.



.jpg)






.png)


