Drilling machine is a general-purpose machine tool with a wide range of uses, which can process parts such as drilling, reaming, flat plane and tapping. When the drilling machine is equipped with process equipment, it can also carry out boring, and when the drilling machine is equipped with a universal worktable, it can also carry out drilling, and reaming.
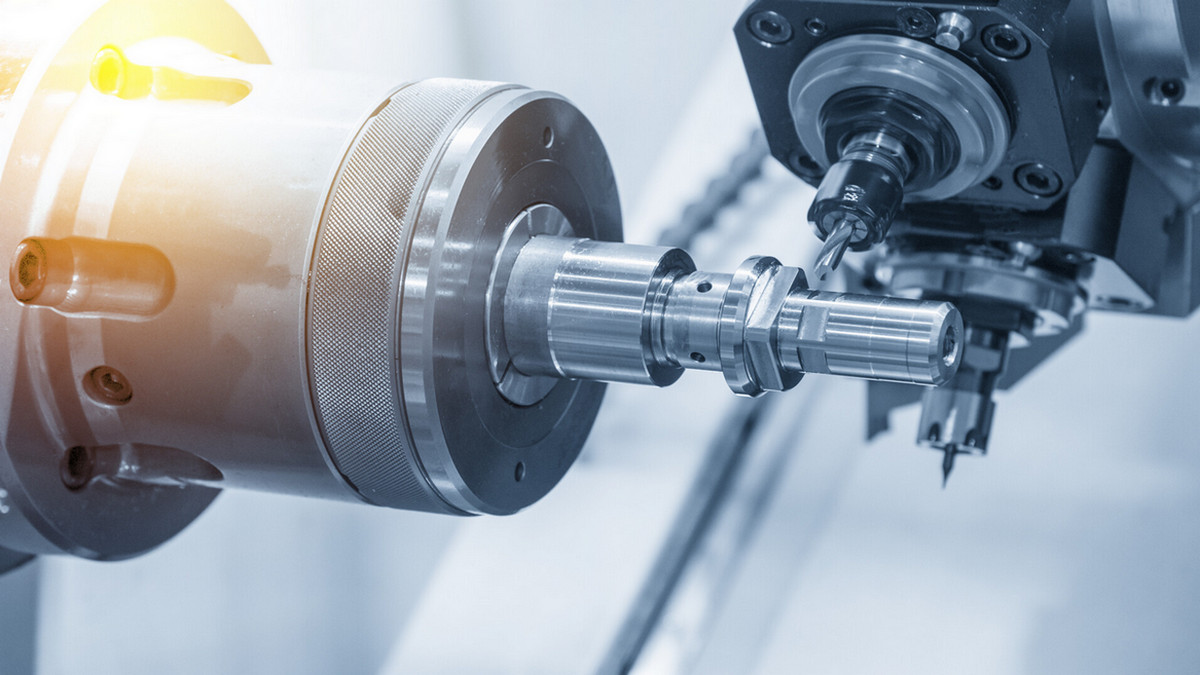
Drilling machine refers to a machine tool that mainly uses a drill to machine holes in a workpiece. Usually, the rotation of the drill bit is the main movement, and the axial movement of the drill bit is the feed movement. The drilling machine has a simple structure and relatively low machining accuracy. It can drill through holes and blind holes, replace special tools, expand, drill holes, ream holes or perform tapping and other processing. During the machining process, the workpiece does not move, the tool is moved, the center of the tool is aligned with the center of the hole, and the tool is rotated (main motion). The feature of the drilling machine is that the workpiece is fixed and the tool rotates and feeds in the direction of the spindle. The operation can be manual or motorized.
Basic Classification of Drilling Machine
The drilling machine mainly uses a drill to process holes on the workpiece (such as drilling, reaming, reaming, tapping, piercing, etc.) bed. Essential equipment for machinery manufacturing and various repair factories. According to the purpose and structure, it is mainly divided into the following categories:
Vertical
The table and headstock can be moved vertically on the column for machining small and medium-sized workpieces.
Desktop
Referred to as bench drill. A small vertical drilling machine with a maximum drilling diameter of 12-15 mm. It is installed on a fitter table, mostly manual drilling, and is often used to process small holes in small workpieces.
Rocker Arm
The spindle box can move on the rocker arm, the rocker arm can rotate and lift, and the workpiece is fixed. It is suitable for processing large, heavy and porous workpieces and is widely used in machinery manufacturing.
Deep Hole Drilling
Specialized machine tools that use deep hole drills to drill holes with a depth much larger than the diameter (such as deep holes in parts such as gun barrels, barrels and machine tool spindles), in order to facilitate chip removal and avoid excessively tall machine tools, generally Horizontal layout, always equipped with coolant conveying device (input coolant from the inside of the tool to the cutting part) and periodic tool retraction and chip removal device.
Center Hole
It is used to machine the center hole at both ends of shaft parts.
Milling and Drilling
The worktable can be moved vertically and horizontally, the drill shaft is arranged vertically, and the drilling machine can be used for milling.
Horizontal Drilling
The main shaft is arranged horizontally, and the headstock can be moved vertically. Generally, it has higher processing efficiency than vertical drilling machines, and can process multiple surfaces at the same time.
Operating Procedures of Drilling Machine
- Before working, it is necessary to comprehensively check whether the operating mechanism of each part is normal, wipe the rocker arm guide rail with fine cotton yarn and fill it with oil according to the lubricating oil grade.
- The rocker arm and spindle box can only be operated after all parts are locked.
- There should be no obstacles within the swing range of the rocker arm.
- Before drilling, the table, workpiece, fixture and cutting tool of the drilling machine must be aligned and tightened.
- Correctly select the spindle speed and feed amount, and do not use overload.
- For drilling beyond the worktable, the workpiece must be stable.
- When the machine tool is running and automatically feeding, it is not allowed to change the speed of tightening and changing. If the speed is changed, it can only be carried out after the spindle is completely stopped.
- Loading and unloading cutting tools and measuring workpieces must be carried out during shutdown. It is not allowed to drill directly with the workpiece by hand, and it is not allowed to operate with gloves.
- If abnormal noise is found during work, it must be stopped immediately for inspection and troubleshooting.
Maintenance and Repair of Drilling Machine
Purpose
Extend the life of drilling machine components and the wear cycle of components, prevent various failures, and improve the average trouble-free working time and service life of the drilling machine.
Maintenance Cycle
Routine maintenance is performed by the drill press operator during or after each job. Regular maintenance is carried out by professional maintenance personnel on a regular basis, once a year or half a year.
Maintain
- The drilling machine should have operating procedures: carry out regular maintenance and maintenance, and pay attention to record and protect the site in case of failure.
- Power requirements.
- The drilling machine should be kept in oil seal when not in use, and covered with sealing film.
- 4. Train and equip corresponding operators, maintenance personnel and programmers.
Drill Press Cleaning
- Wipe the drill floor, bed, guide rail, screw and operating handle. Keep the bed and its surroundings clean and free of oil.
- Remove the burrs on the guide rail and the impurities of the screw drilling slag.
- Disassemble and clean the oil felt.
- Remove rust from all parts of the drilling machine and protect the painted surface.
CNC Maintenance
- Strictly abide by the operating procedures and daily maintenance system.
- Prevent dust from entering the CNC device: floating dust and metal powder can easily cause the insulation resistance between components to drop, resulting in failure or even damage to components.
- Regularly clean the cooling and ventilation system of the CNC cabinet.
- Always monitor the grid voltage of the CNC system: the grid voltage range is 85%~110% of the rated value.
- Regularly replace the battery for memory.
- Maintenance when the CNC system is not used for a long time: often power on the CNC system or make the drilling machine run the warm-up program.
- Maintenance of spare circuit boards.
Parts Maintenance- Maintenance of lead screw and guide rail
- Maintenance of the drive shaft
Pneumatic Maintenance- Remove impurities and moisture from compressed air.
- Check the oil supply of the lubricator in the system.
- Maintain the sealing of the system.
- Pay attention to adjust the working pressure.
- Clean or replace pneumatic components and filter elements.
Cutting Fluid Supply Overhaul- Regularly clean the water pump, filter and cutting fluid tank.
- Check whether the cutting fluid pipeline and nozzle are unblocked and whether there is leakage.
- Regularly replace the cutting fluid.
- Regularly check the concentration and pH of the cutting fluid.





.jpg)







.png)