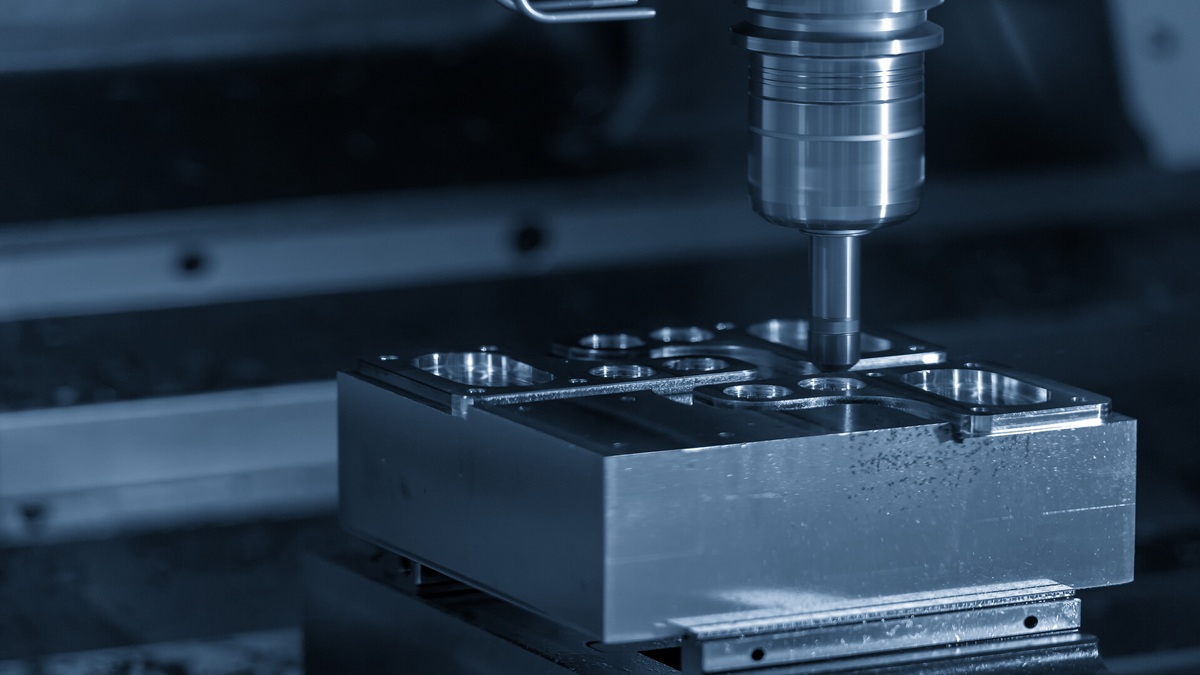
The core requirements for food processing equipment lie in safety, efficiency, and durability. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology, with its precision and automation advantages, has become a key enabler in the manufacturing of slicers, packaging machines, mixers, and other equipment. With the global food processing equipment market projected to grow from USD 55 billion in 2023 to USD 75 billion by 2030 (a CAGR of approximately 4.5%), CNC is driving the industry toward greater intelligence and efficiency.
Practical Cases: How CNC Enhances Food Processing Equipment Performance
Case 1: JBT Corporation Slicer Blades
JBT Corporation uses CNC lathes to machine 316L stainless steel slicer blades with a precision tolerance of ±0.001 inches, ensuring sharp edges and an ultra-smooth surface (Ra 0.1 μm). This reduces meat and vegetable residue, meets FDA hygiene standards, and shortens cleaning time by about 15%, boosting overall production line efficiency.
Case 2: Tetra Pak High-Speed Packaging Molds
Tetra Pak employs five-axis CNC milling machines to manufacture beverage packaging molds with a tolerance of ±0.01 mm, supporting high-speed production of 10,000 packages per hour. CNC machining and special polishing reduce material waste by approximately 8% and ensure reliable sealing, meeting strict aseptic packaging standards.
Case 3: SPX FLOW Mixing Equipment
SPX FLOW utilizes CNC technology to machine high-shear mixer blades with precise control of blade angles (±0.2°) and thickness, ensuring uniform mixing while reducing energy consumption by about 15%. These blades, made from food-grade alloys, are corrosion-resistant and extend equipment lifespan, particularly suitable for sauces and dairy processing.
Unique Advantages of CNC Technology
CNC technology offers multiple benefits for food processing equipment. It enables micron-level precision (around ±0.025 mm) for parts, ensuring consistent and reliable components, reducing defects, and complying with ISO 22000 and other food safety standards. CNC machining of stainless steel or food-grade plastics (e.g., POM) achieves ultra-smooth surfaces (Ra ≤ 0.2 μm), reducing bacterial growth and enhancing hygiene. Automation reduces manual labor, increases production efficiency by approximately 20%, and, when integrated with IoT, enables real-time monitoring that can lower maintenance costs by about 10%. Its flexibility also supports rapid prototyping and customized designs, such as specialized blades or molds for unique food shapes, shortening development cycles by roughly 30%, making food processing equipment both efficient and reliable.
Conclusion
When selecting CNC-processed equipment, buyers should prioritize 316L stainless steel or food-grade plastics that meet FDA, EU, and ISO 22000 standards. Surface finish (Ra ≤ 0.4 μm) and corrosion resistance are key to reducing cleaning frequency and long-term maintenance costs. Equipment supporting IoT and automation improves production efficiency and enables smart data management, while the supplier’s technical capability, range of CNC machines (e.g., 5-axis mills), and after-sales service determine operational stability. With the rise of smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0, choosing CNC equipment that supports rapid prototyping and small-batch production allows companies to respond flexibly to market demands while ensuring efficiency, quality, and future competitiveness.

.jpg)
.jpg)









.jpg)