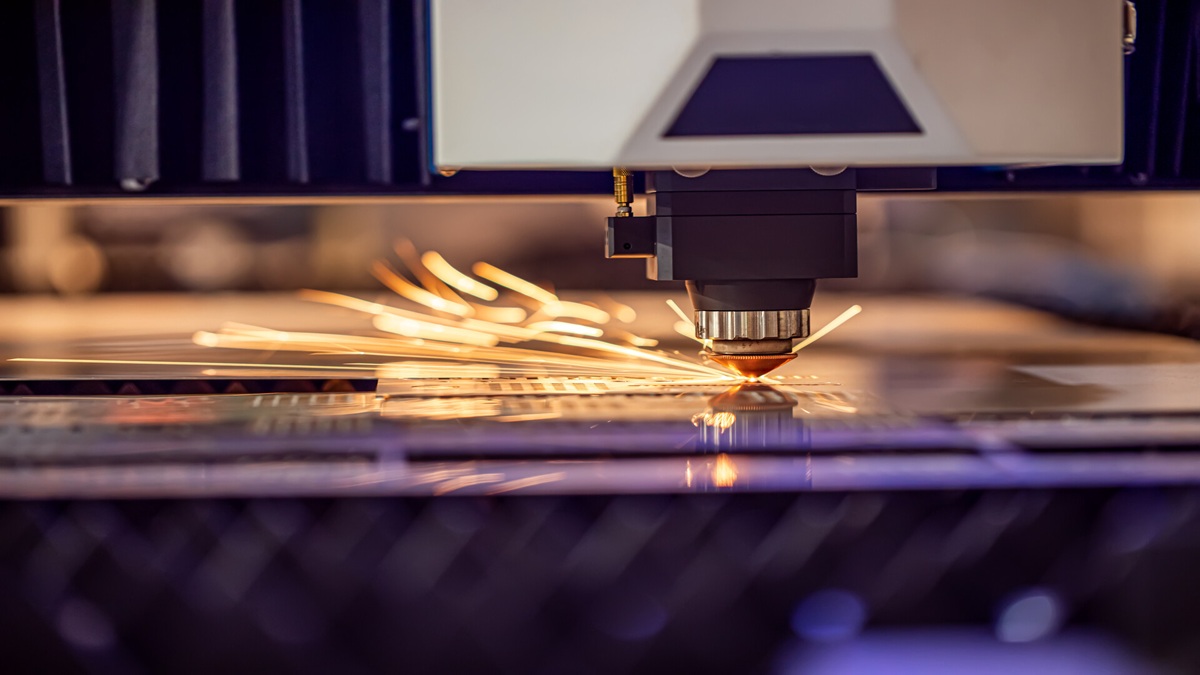
Metal stamping refers to the use of the power of punching machinery and the use of molds as metal plate forming tools to produce punching separation or plastic deformation effects to achieve the production technology of parts in terms of size, shape, and performance requirements.
What Is Stamping Technology?
Stamping is a manufacturing technology that can make sheets or plates of different thicknesses into the desired shape by mechanical stamping or ramming and does not change the thickness of the original material during the manufacturing process. Stamping technology is widely used in manufacturing engineering for three-dimensional components, cutting, or other special surface requirements.
Freely deformable metal
Metal has excellent strength, so it is often used as a structural member that requires strength. At the same time, we also found that when the applied stress (that is, the force per unit area) exceeds its tensile strength, the metal will not break immediately like brittle materials such as ceramics or bricks, but will deform. That is to say, metal has plasticity, we call it plastic deformation. Every metal has different deformability, the most obvious example is gold. Utilizing the plastic deformation characteristics of metal, the metal is formed into various shapes.
How can we plastically deform the seemingly strong metal? Then you have to use die steel that is stronger than metal. The mold steel is made into upper and lower molds according to the shape to be formed, and then the upper and lower molds are opened and the raw materials are placed, and then the molds are fixed on a device called a punch. Let the punch provide the force required for forming, and drive the mold to close and open the mold up and down. The mold is closed to form the material, and the mold is opened to allow the raw materials to enter and exit. The punch, mold, and raw materials constitute a set of stamping forming systems. Under strong pressure, even very strong metals have to deform with the shape of the mold.
Brief Description of Stamping Process
The most common stamping processes include punching, bending, and drawing. Take the key to be used every day as an example. If you design a lower female mold with the same shape as its inner hole, and an upper punch with the same shape as it but a smaller upper punch, place the sheet on the female mold and use a punch to fix it on the upper punch punches down through the sheet to get the key of the desired shape. Such as the use of automated punch production, two to three hundred pieces or more can be produced in one minute. This is the simplest example of punching. In order to enhance the required functions or quality of the product, some subsequent machining procedures are still needed.
Regarding the bending process, it can be imagined that the upper and lower molds first press the sheet metal with the spring force, and then use the punch to apply force to the part that needs to be bent. An example of the bending process can be illustrated by the strap of a watch. A general metal watchband is made of stainless steel and is divided into two parts, a chain strap, and a buckle. When you look at the fastener, you will find that it contains 3 plates, and the inside of the joint also contains a hosel and a spring. Each piece of the plate must be bent or curled in a certain part for the function of a buckle. A closer inspection will find that it also uses other forming techniques. The part of the chain strap is also a series of punching, bending, and pressing of the plate to make a strap with the function of the chain and beautiful. Of course, if you disassemble the watch, you will find more stamped parts distributed in it. Another common example is the stapler. It is obvious that its structural parts are made by bending metal plates.
Regarding the drawing method, you can imagine a large round plate with a diameter of about 50 cm and a thickness of 0.2 cm. It is placed on a female mold with an inner hole diameter of 30 cm. The plate is pressed by a spring force in the range of 30 to 50 cm in diameter. And then use a punch with a diameter of about 29.6 cm to shape the sheet down. The plate will change from a disc shape to the shape of a can body, and the peripheral material is pulled into the female die hole by the punch to become the straight wall part of the can body. If you think the diameter is too large, you can use another set of female molds and punches with a smaller inner diameter and smaller diameter to form again. Such a forming method is called drawing.
The technology of stamping is not as simple as the above, it includes more different production methods. In order to obtain better quality, every processing method must establish standards or be changed to keep improving. A product is composed of dozens or even hundreds of parts. If the quality of one of the parts is quite different, for example, the size of each is different, then it will be impossible to assemble the product by automated means, or even Manual assembly can't be installed, and it will cause the failure of the product. Therefore, today's industry players are competing for the quality of parts processing and the reduction of manufacturing costs. Those who can produce the same or even higher quality parts at a lower cost will eventually win.
Brief Introduction of Stamping Technology
Regarding the punching process technology, take punching a round hole as an example. Generally, due to the characteristics of the material itself, half of the section of the punching surface is a torn surface. However, the use of round holes often requires that all sections must be smooth. For this requirement, punching technology has developed many different methods, such as punching first, and then scraping to remove the tears left by punching cracked surface. It is also possible to trim the right-angled edge of the punching die into a very small rounded edge or apply a large calculated pressure on the material around the punching part, and then perform precision blanking and punching. Different punching methods have different qualities of punching surface and production cost. The choice of punching method depends on the evaluation and selection of the producer.
When the part is bent, scratches are often caused by the friction between the mold and the material. At this time, you may think that the relative movement between the mold and the sheet should be less than the sliding friction during rolling friction. That's right, adding a roller to the part where the bending punch contacts the blank can effectively improve the scratch problem. In addition, you may also have experience. When you bend something, you will often find that it will bounce back a little bit. This is because every material is elastic. This problem also occurs when the metal is bent. Stamping engineering has also developed various ways to improve this problem.
In order to make the formed parts have the correct dimensions and be perfectly assembled and matched with other parts, the most direct way is to "turn over". For example, if the material rebounds by 2 degrees when bent at a right angle, it can be bent to 88 degrees during bending. When the mold leaves the blank, the workpiece will rebound to the target value of 90 degrees. The material will rebound because of the plastic deformation of the bending part, which causes the internal stress in this area. When the mold is released, the internal stress causes the material to produce a recovery action and cause the rebound. Therefore, the mold is used to compress this area to destroy its stress. Status can also effectively overcome this problem. You can also bend 45 degrees first, and then bend 90 degrees after a part of the rebound. From this, we can discover how engineers try their best to overcome problems when facing problems, and they must conform to the principles of physics even if they are ingenious.
Regarding drawing a cup-shaped tank, imagine how a tank with a larger diameter is willing to shrink into space with a smaller diameter? The outer blank material and the inner tank body resist each other with tension, and improper design will cause the material to break the mold. Therefore, how to choose the gradually smaller diameter and the fillet of the mold entrance, and formulate design criteria with different materials, his deep knowledge in the extension engineering. Under the global competition, in order to improve the quality of products and be competitive at the same time, stamping technology has undergone extreme evolution and development.
Automated production line
When it comes to stamping, we must first understand what is a continuous die? If a complex part requires extremely complicated stamping processing, for example, it requires 10 stamping steps, which may include punching, bending, and drawing. If it is processed separately step by step, 10 types of equipment and 10 manual workers, and each operator needs to feed and unload, obviously, the cost will be high and the production efficiency will be low.
Therefore, under the permission of punching capacity and mold space, rolls can be used as raw materials. The automatic feeder sends the materials to the punching mold for processing. All stamping processes are integrated into a set of molds, and the rolls are quantitatively transferred gradually. Forward. Each amount of blank material will be formed through all the stamping procedures. During the forming process, the blank material will be connected to the belt, and finally punched and separated. In this way, all forming projects can be completed on one punching machine, so the cost, efficiency, and product quality can be greatly improved.
The number of parts that can be produced per minute depends on the product size, shape, and punching equipment capacity, ranging from dozens of pieces to thousands or even 2,000 pieces. Of course, the product must reach a certain number to have economic benefits, so continuous die is the main production type of today's mass production stamping production line.
After decades of development, stamping production technology has developed to the extreme in both breadth and depth. The improvement of punching equipment capabilities and characteristics, the diversity of mold design technology and processing precision, the mastery, and improvement of raw material formability, and the advancement of peripheral technologies such as automation or lubrication and testing constitute a complete and mature processing system, Especially Japan is the most representative.
Punching machines can be divided into two types. They are mechanical and hydraulic power. Metal stamping machines stamp, form, cast, and cut metal plates. In order to form a three-dimensional shape, a complete metal sheet is placed inside the mold, and then a mechanical press is able to make the article. The metal thickness of these plates can reach a quarter of an inch, and they are formed into specially designated shapes of different sizes. Zinc, copper, aluminum, and stainless steel are common metals used in different industries to perform metal stamping procedures.
Presses for metal stampings can manufacture a wide variety of items, and they can perform operations including metal stamping, punching, and four sliding forming operations. Blanking, also known as fine blanking, is usually the first die that is guided to a fully formed part die. The metal imprint is like the title. It can be used to make coins from metal. However, it also has other functions. The forming of the four sliders incorporates a mixture of stamping and framing procedures, making more complex items especially effective for smaller parts.
In recent years, metal stamping has replaced all other metal forming techniques. For example, forging and die-casting processes are being replaced, because metal stamping has relatively low production costs. Articles made by the stamping process can be stronger and more durable than those made in other metal forming methods. Metal stamping is part of a mixed commercial enterprise because these parts can be efficiently produced at a very advantageous rate, which is useful for general production time and expense.
Metal stamping operating:
Metal stamping processes such as bending processing, punching, flange processing, drawing processing, hemming processing, shrinking processing, embossing processing, embossing processing, drawing processing, crimping processing, etc.
Industrial Applications of Metal Stamping Process
Metal stamping can be connected to a huge variety of materials, considering that they are one of the metal processing features of various applications in various industries. The metal stamping process may require forming, forming, and transforming common base metals into uncommon alloys for special preferences related to its application. Several commercial industries require the thermal or electrical conductivity of beryllium copper in various fields, such as aviation, electricity, and defense-related businesses, or the high-quality operation of steel and its numerous automotive composite materials. Metal stamping is used in various industries. Such as agriculture and cultivation, home appliances, weapons and ammunition, aerospace, power storage, building construction, electronics, vehicle industry, lawn equipment, various lighting projects, locking hardware, medical uses, power tools and equipment, marine uses, shipbuilding, water pipes tools, etc., used to manufacture metal parts in various machines in various industries.








.png)




