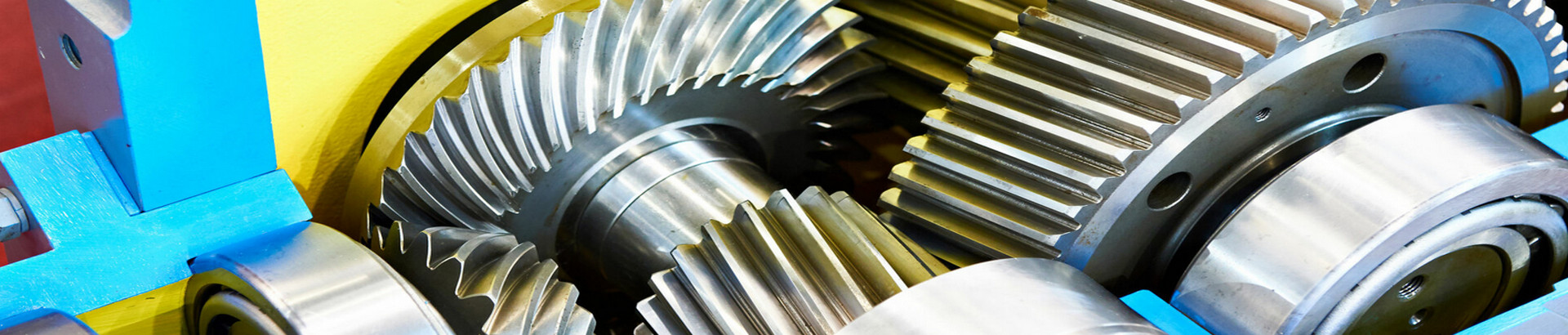
Speed reducers are powerful mechanical devices generally used in machining tools to multiply the force or torque generated by an input power source, thereby increasing the usable force, enhancing the performance and precision of the machining tool. They are also used in material handling systems such as conveyor belts and lifting mechanisms to control the speed of material transfer and manage heavy loads efficiently. By multiplying the available output force, they enable the use of a reduced input power source, resulting in cost savings for machine tool investments. When choosing the appropriate speed reducer, the torque, speed, and horsepower of the input, as well as the mounting configuration, efficiency, and required lifetime all need to be considered. The quality of the machine chosen will also be reflected in the amount of backlash, transmission error, torsional rigidity, and inertia experienced during machining.
Gear Configurations
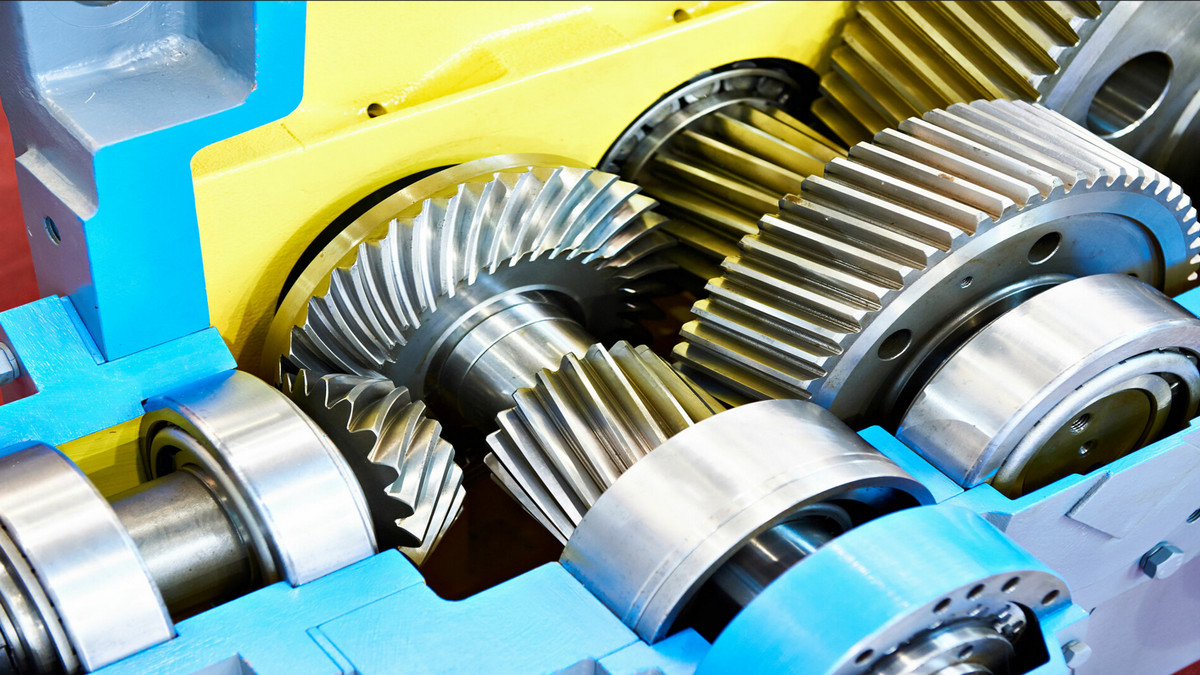
While there is a wide variety of mechanical speed-reducing devices available, including belt-driven devices, friction drives, and electrical devices that can change the motor speed, the most common type of speed reducers use a set of gear drives and gearboxes with various gear configurations. The gears may be configured in-line, where the output shaft is in line with the input shaft, or with the output shaft at an angle from the input, most commonly at a 90-degree angle to the input.
Helical and Spur Gears
In-line reducers are commonly made up of either helical or spur gears. Spur gears have straight teeth mounted on a cylindrical disk, where the teeth are parallel to the axis of the gear. Helical gears, on the other hand, have teeth that are inclined at an angle to the gear axis. When helical gears mesh, the contact between the teeth is gradual and occurs at an angle, resulting in smoother and quieter operation compared to spur gears. Helical gears can handle higher loads and provide better tooth engagement, reducing the risk of teeth chipping. However, they are slightly more complex to manufacture than spur gears. Helical and spur reducers are generally the most economical choices.
Planetary Gears
A planetary gear consists of a central gear (sun gear) surrounded by multiple smaller gears (planet gears) that rotate around it and mesh with an outer ring gear. Planetary gear reducers offer high torque density due to multiple gears sharing the load and are generally more efficient than worm gear reducers. A planetary gear configuration generally provides the highest torque in a compact arrangement and is well-suited for applications where space is limited.
Offset Angle Designs
Right-angle designs are typically made with worm gearing or bevel gearing. A worm gear consists of a cylindrical screw (the worm) that meshes with a toothed wheel (the worm gear). Motion is transferred at a right angle, and the contact between the worm and worm gear occurs along a single line. A worm gear configuration offers a very cost-effective reduction solution but is usually limited to a minimum 5:1 speed reduction ratio and becomes less efficient as ratios increase.
Bevel reducers consist of two intersecting shafts with gears that have conical-shaped teeth, meshing between non-parallel shafts. The gears are versatile and can be used to transfer motion between non-parallel and intersecting shafts, often at 90-degree angles. Bevel gears can be more efficient than worm gears, especially in applications requiring 90-degree turns, but they have an effective speed reduction upper limit of 6:1.
Features to Look for When Purchasing a Reducer
Torque Rating
The amount of torque needed is perhaps the most important criterion, as this determines the amount of work the speed reducer must perform. Consideration should be made for physical conditions such as friction, gravity, load sizes, and inertia encountered during operations. Be sure that the chosen reducer can handle peak loads without compromising performance.
Efficiency and Precision
Opting for reducers that provide accurate speed control not only increases precision but can also help maximize efficiency, thus minimizing energy loss during operation. The main power source typically operates at a specific optimal speed. Choosing the correct speed reducer ratio and the resulting torque change is merely a matter of dividing the motor speed by output speed. Then, the proper motor size can be found by using a standard horsepower conversion formula.
Durability and Reliability
Machining environments can be harsh, with exposure to dust, debris, and varying temperatures. Choose reducers with durable materials and robust construction to withstand these conditions and ensure long-term reliability.
Other factors to take into account include the length of workdays, numbers of starts and stops, load characteristics, and power sources. Most reducers are rated for maximum torque, and the machine's lifetime is not related so much to gear or shaft strength but to the bearing life. Because bearings must support heavy loads, exceeding the maximum load rating will significantly decrease gearbox life.
Mounting Configurations
Some reducers offer versatile mounting configurations, providing flexibility in installation. Consider the available space and mounting requirements of your machinery. Many gearboxes are designed with the motor mounted directly to the reducer, eliminating the need for a separate mounting of the motor, thus reducing space. This is usually advisable for machines with smaller motors.
Shaft orientation is important for maintenance purposes as well. In many applications, it is desirable to have either the input or output shaft mounted vertically, but with this orientation, greater care must be taken to assure proper gear and bearing lubrication. Whenever a shaft is vertically mounted, it is important to determine if an alternate lubrication method is necessary.
Maintenance Considerations
Even well-designed and engineered speed reducers are subject to wear and eventual failure. To maximize life, proper maintenance procedures should include routine lubrication and oil change. Oil and grease used for lubrication are highly prone to deterioration under the extremely high temperatures, pressure, and shearing effect of gear meshing.
Understanding the general principles behind reducers, recognizing their diverse applications, and making informed decisions when purchasing them are essential steps toward achieving optimal operational performance, productivity, and product reliability.