A method of transmitting rotational force between two separated shafts using pulleys and belts. The rotation speed ratio is inversely proportional to the diameter of the two pulleys, and it can slide when the load is excessive to prevent mechanical damage.
What is a Belt Drive?
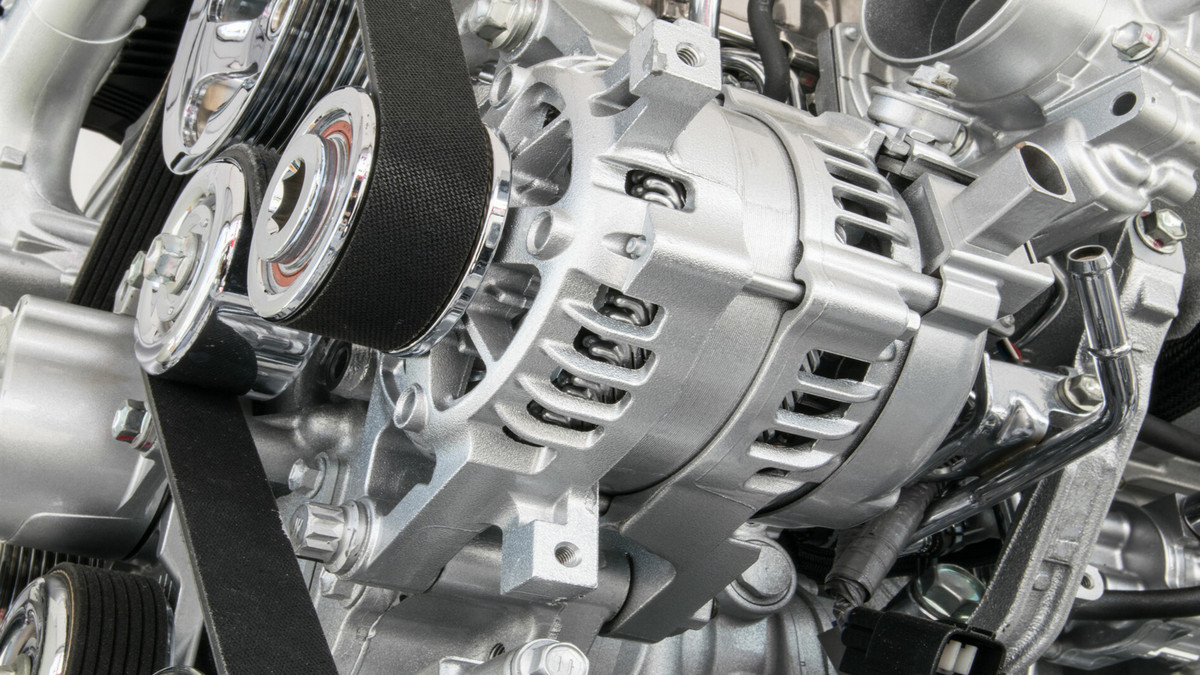
The basic principle of belt drive:
A belt drive is a mechanical transmission that uses a flexible belt tensioned on a pulley for motion or power transmission. According to the different transmission principles, there are friction-type belt drives that rely on the friction between the belt and the pulley, and there are synchronous belt drives that rely on the intermeshing transmission between the belt and the teeth on the pulley.
The stress on the belt drive when working:
- The stress generated by the tension of the tight and loose edges.
- Stress caused by centrifugal force.
- The bending stress generated by the belt bending on the pulley.
What are the Classifications and Uses of Drive Belts?
According to different uses, belt transmission can be divided into general industrial transmission belts, automotive transmission belts, agricultural machinery transmission belts, and household appliances transmission belts. Friction belts are divided into flat belts, V belts, and special belts (V-ribbed belts, synchronous belts) according to their different cross-sectional shapes.
- Flat belt:
When the flat belt drive works, the belt is sleeved on the smooth wheel surface, and the transmission is carried out by the friction between the belt and the wheel surface. The transmission types include open transmission, cross-transmission, semi-cross transmission, etc., which respectively meet the needs of different relative positions and different rotation directions of the driving shaft and the driven shaft. The flat belt drive has a simple structure, but is easy to slip, and is usually used for transmission with a transmission ratio of about 3.
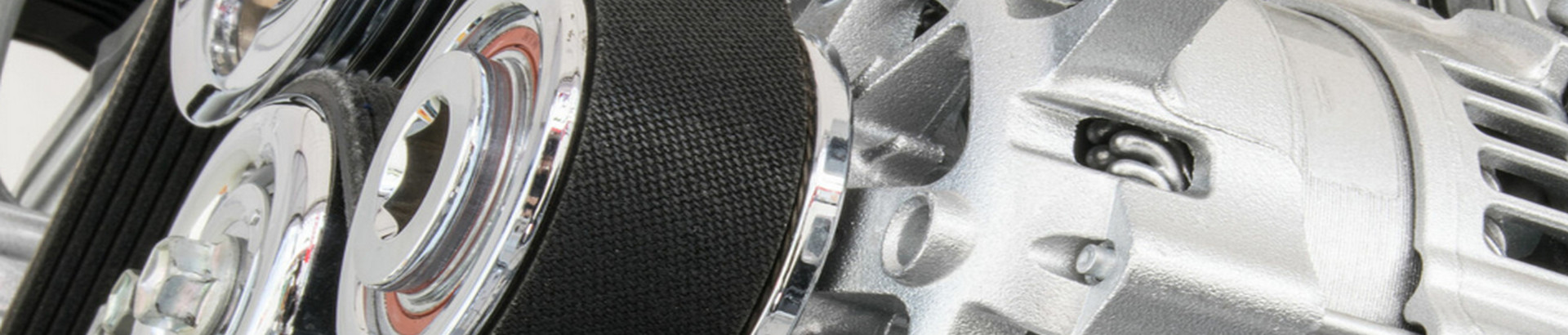
- Poly V-belts:
The flexibility is good and the back of the belt can also be used to transfer power. If the containment angle around each driven pulley is large enough, one such belt can simultaneously drive several accessories of the vehicle. It has 5 kinds of sections such as PH, PJ, PK, PL, and PM for selection, among which the PK section has been widely used in automobiles in recent years. This type of belt allows the use of narrower pulleys than narrow V-belts. To be able to transmit the same power, the preload of this kind of belt is preferably about 20% larger than that of the narrow V-belt.
- Timing belt:
This is a special belt drive. The working surface of the belt is made into a tooth shape, and the rim surface of the pulley is also made into a corresponding tooth shape. The belt and the pulley are mainly driven by meshing. Synchronous toothed belts generally use thin steel wire ropes as the strength layer and are covered with polychloroprene or neoprene. The center line of the tension layer is determined as the pitch line of the belt, and the perimeter of the belt line is the nominal length. The basic parameters of the band are the period p and the modulus m. The circumferential pitch p is equal to the dimension measured along the pitch line between the corresponding points of two adjacent teeth, and the modulus is m=p/π.
Transmission features are:
- The tension layer made of steel wire rope deforms very little after being loaded, the circumference of the toothed belt is unchanged, there is no relative sliding between the belt and the pulley, and the transmission ratio is constantly accurate.
- The toothed belt is thin and light and can be used in high-speed situations. The linear speed during transmission can reach 40 m/s, the transmission ratio can reach 10, and the transmission efficiency can reach 98%.
- Compact structure and good wear resistance.
- Due to the small pre-tension, the bearing capacity is also small. The manufacturing and installation accuracy requirements are very high, and the center distance is required to be strict, so the cost is high. A synchronous toothed belt drive is mainly used in occasions requiring accurate transmission ratios, such as external equipment in computers, movie projectors, video recorders, and textile machinery.
- V-belt:
The V-belt is the most used belt drive for robots. When the V-belt drive works, the belt is placed in the corresponding groove on the pulley, and the transmission is realized by the friction between the belt and the two walls of the groove. V-belts are usually used in combination with a corresponding number of grooves on the pulley. When the V-belt is used for transmission, the belt and the wheel are in good contact, the slippage is small, the transmission ratio is relatively stable, and the operation is stable. V-belt transmission is suitable for occasions with short center distance and large transmission ratio, and can also work well in vertical and inclined transmission.
Advantages of Belt Drive:
- It is suitable for the large center distance, the transmission belt has good elasticity, can buffer, and absorb vibration, especially the V-belt has no joint, the transmission is relatively stable, and the noise is small.
- When overloaded, the belt slips on the pulley, which can prevent other components from being damaged. The structure is simple, the manufacture and maintenance are convenient, and the cost is low.
- Simple structure, no rust, lightweight, longer maintenance period than chains, easy maintenance, and no need for lubrication.
Disadvantages of Belt Drive:
- The outer dimension of the transmission is large, and the force on the shaft is large due to the need for tension.
- There is elastic sliding in the work, and the speed ratio relationship between the driving shaft and the driven shaft cannot be accurately maintained.
- The life of the belt is short, the transmission efficiency is reduced, and the belt transmission may be electrified due to friction, resulting in sparks, so it cannot be used in flammable and explosive occasions.
- The wider is easy to accumulate dust, may slip, the damping of the cold car transmission is relatively large, the heat resistance is poor, the overload resistance is poor, it is easy to age, the transmission ratio has no chain, and the shaft transmission is high.









.png)



