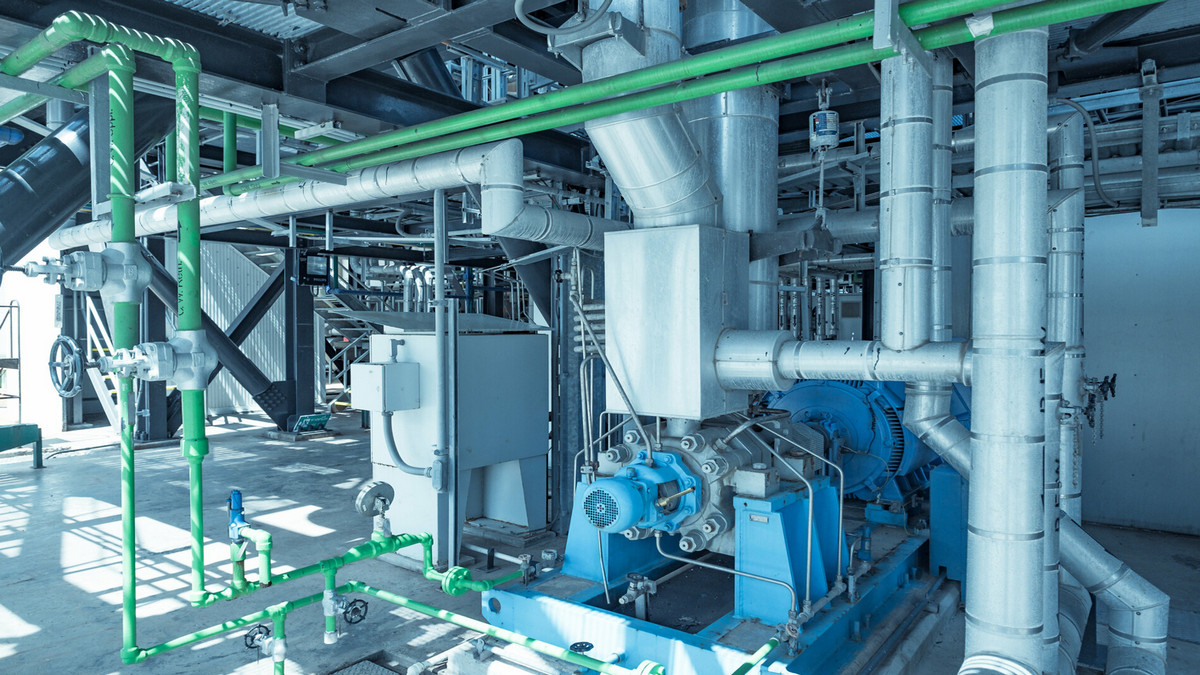
The internal mixer is an internal mixer widely used in various industries. It can be used in a multi-step mixing process and is common in rubber manufacturing.
What is an Internal Mixer?
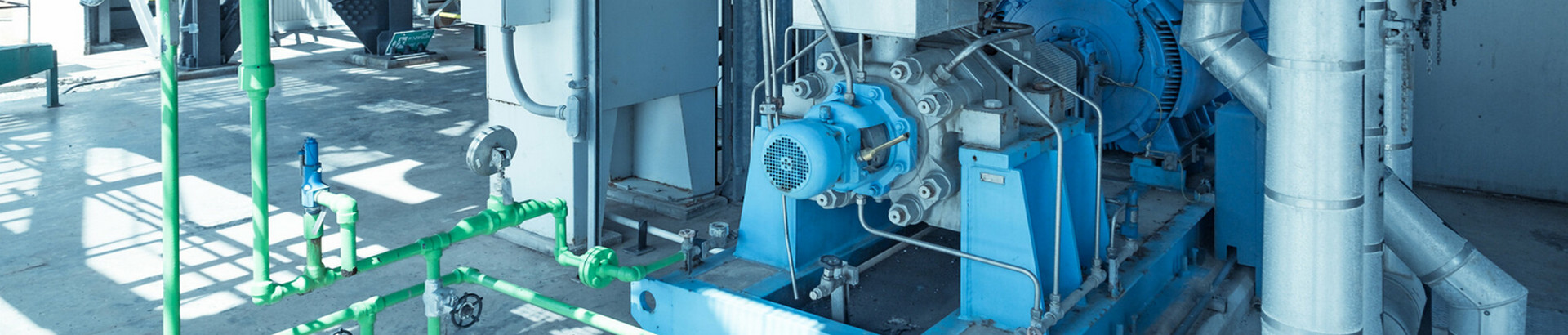
An internal mixer is a kind of machine that is equipped with a pair of rotors with a specific shape and rotates relative to each other. It is a machine for plasticizing and mixing polymer materials intermittently in a closed state with adjustable temperature and pressure. It is mainly composed of an internal mixing chamber, and rotors. It is composed of a rotor sealing device, feeding, and pressing device, unloading device, transmission device, and machine base. Internal mixer feeding and discharging are easy to manage for applications where mix quality and consistency are important.
The Basic Structure of the Mixer:
The main components of the mixer include a mixing chamber, rotor, upper bolt, lower bolt, cooling system, lubrication system, sealing device, and transmission device. The mixing chamber is the working part of the mixer, and two rotors rotate relative to each other at different speeds for plasticizing or mixing.
- Mixing chamber: The mixing chamber is composed of two sets of C-shaped heating chambers and two rollers. The outer side of the mixing chamber is equipped with a double circulating water jacket, which is convenient for cooling or heating.
- Roller: Made of medium carbon steel, the top of the roller blade is welded with STELLITE high wear-resistant metal, and both ends are sprayed.
- Welding tungsten carbide alloy steel: The roller is hollow and can be cooled by water to adjust the temperature of the raw material in the mixing chamber.
- Sealing ring device: Triangular fork structure, hydraulic self-adjusting type, with eight-port and twelve-port high-pressure oiler.
- Pneumatic cylinder: Welded with steel plate or cast with FC25 cast iron. In addition to fixing the large cylinder, the cylinder block is supported at two points inside to assist the disadvantage of the large cylinder having a long stroke and being unable to stabilize its center.
- Reducer: It is a fully enclosed three-stage reducer, a heavy-duty gear reducer with a single input shaft and double output shaft, and the safety factor of gear design is 1.8 times.
- Operation panel: Including ammeter, temperature controller, loop-type operation timer, buzzer, start or stop button, and operation indicator light of each unit.
The Working Principle of the Mixer:
Internal mixers are mainly used for plasticizing and mixing rubber. An internal mixer is a kind of high-strength intermittent mixing equipment developed based on an open mixer. It shows a series of features superior to the open mill in the rubber mixing process, such as large mixing capacity, short time, and high production efficiency. It can better overcome dust flying, reduce the loss of compounding agents, and improve product quality and work surroundings. Safe and convenient operation, reduce labor intensity. It is beneficial to realize mechanical and automatic operation, etc. Therefore, the appearance of the internal mixer is an important achievement of rubber machinery, and it is still typical important equipment in plasticizing and mixing, and it is developing and improving.
The internal mixer is generally composed of an internal mixing chamber, two relatively rotating rotors, an upper top bolt, a lower top bolt, a temperature measurement system, a heating, and cooling system, an exhaust system, a safety device, a discharge device, and a recording device. The surface of the rotor has helical ridges, including two, four, six, etc., and the cross-sectional geometry of the rotor is triangular, cylindrical, or oval, and there are two types of tangential and meshing. The temperature measurement system is composed of thermocouples, which are mainly used to measure the temperature change in the mixing chamber during the mixing process. The heating and cooling system is mainly to control the temperature of the rotor and the wall surface of the mixing chamber.
When the mixer is working, the two rotors rotate relative to each other, and the material from the feeding port is clamped and brought into the roll gap to be squeezed and cut by the rotor. Along the gap between the front and rear chamber walls and the rotor and back to the top of the nip. During the flow around the rotor, the material is sheared and rubbed everywhere. The temperature of the rubber material rises sharply, the viscosity decreases, and the wettability of the rubber on the surface of the compounding agent is increased so that the rubber and the compounding agent surface are fully contacted.
The batch of compounding agents passes through the gap between the rotor and the rotor, the rotor and the upper and lower top bolts, and the inner wall of the mixer together with the rubber compound. It is sheared and broken, surrounded by stretched and deformed rubber, and stabilized in a broken state. At the same time, the ridges on the rotor make the rubber material move along the axial direction of the rotor, which plays the role of stirring and mixing so that the compounding agent is evenly mixed in the rubber material. The compounding agent is repeatedly cut and broken. The rubber compound is repeatedly deformed and restored, and the rotor ridges are continuously stirred. The compounding agent is uniformly dispersed in the compound and reaches a certain degree of dispersion. Due to the shearing effect of the rubber compound during the mixing of the internal mixer being much greater than that of the open mixer, and the high temperature of rubber mixing, the efficiency of the rubber mixture in the internal mixer is much higher than in the open mixer.
Operations suitable for standard stirring:
- Regrind
- Final mix
- Masterbatch mix
Internal Mixer Gearbox for Rubber Production:
Internal mixer gearboxes are standard helical gearboxes that must be able to withstand high loads at variable speeds. This is because the rotors used in internal mixers and other internal batch mixers rely on variable speed and high pressure to mix materials of different densities.
Internal mixers are the most used mixers by manufacturers of rubber products. Since the mixture is viscous, the mixer needs a powerful motor and gearbox to maintain a smooth and constant flow. If an internal mixer or other internal batch mixer used in rubber manufacturing fails, it can be difficult to clear the blockage and restart the mixer, resulting in lost production.
Rubber Manufacturing Requires Reliability and Efficiency:
In the rubber manufacturing and processing industry, success and profitability require reliable and efficient mixing equipment. Malfunctioning gearboxes and drives of internal mixers and power mixers caused blockages that stopped production and were difficult to clear. Rubber manufacturers need to provide customers with consistent and uniform products. For example, car tires and conveyor belts can only be made of high-quality materials. Reliable and efficient internal mixers and heavy-duty mixer gearboxes ensure consistent output to meet customer quality requirements.
Mixer Operation Method:
- According to the capacity of the mixing chamber of the internal mixer and the appropriate filling factor (0.6-0.7), calculate the amount of one-time mixing and the actual formula.
- According to the actual formula, accurately weigh the amount of various raw materials in the formula, place the raw rubber, small material, reinforcing agent or filler, liquid softener, and sulfur separately, and arrange them in order on the shelf.
- Turn on the power switch and heating switch of the mixer, preheat the mixer, and check whether the air pressure, water pressure, and voltage meet the process requirements, and check whether the temperature measurement system, timing device, and power system indications and records are normal.
- After the mixer is preheated, stabilize for a while, and prepare for rubber mixing.
- Lift the top bolt, put the raw rubber that has been cut into small pieces into the mixer from the feeding port, drop the top bolt, and mix the rubber for 1min.
- Add small materials, and drop the top bolt for mixing.
- Add carbon black or filler, and drop the top bolt for mixing.
- Lift the top bolt, add liquid softener, drop the top bolt, and mix.
- To remove the glue, use a thermocouple thermometer to measure the temperature of the rubber compound, record the initial temperature of the mixing chamber, the temperature of the mixing chamber and the temperature of the glue removal at the end of mixing, the maximum power, and the rotational speed of the rotor.
- Adjust the roll distance of the open mill to 3.8mm, turn on the power switch, make the mill run, open the circulating water valve, and then throw the rubber material discharged from the internal mixer into the open mill to wrap the rolls, wait for the glue When the temperature of the material drops below 110°C, add sulfur, and cut the left and right knives twice.
- Adjust the roll distance of the open mill to 0.5mm, put in the rubber compound, make a triangular bag, and make a thin pass 5 times, adjust the roll distance to about 2.4mm, put in the rubber roll, and wait until the surface is smooth and no bubbles. Weigh the total mass of the rubber compound, put it on a flat and clean metal surface and cool it to room temperature, put a label on it to indicate the compound formula number and mixing date, and park it for later use.
- Record the mixing process test report of each batch of the internal mixer: record the temperature at the beginning of mixing, mixing time, rotor speed, top bolt pressure, discharge temperature, power consumption, and the difference between the quality of the mixed rubber and the total quality of the raw materials value and mixer type.









.png)



