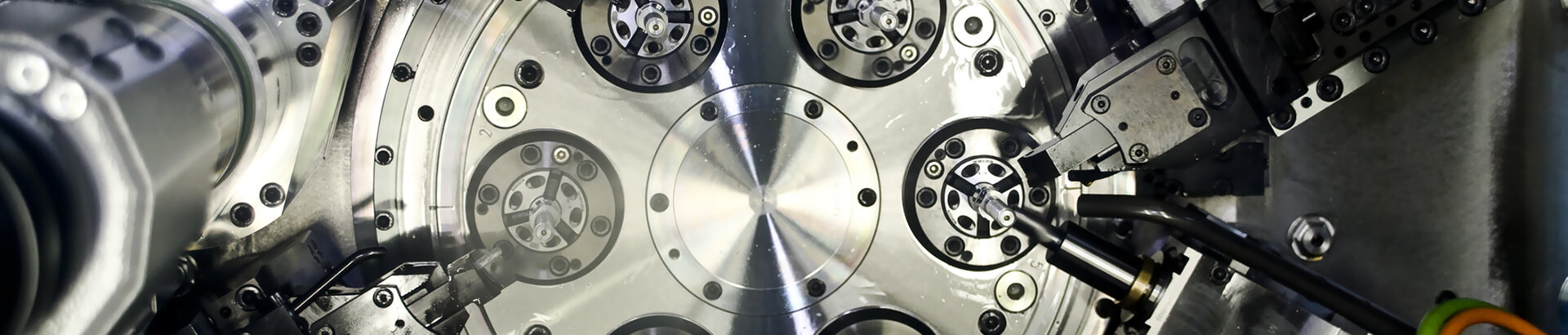
One of the main tenets of Industry 4.0 is data collection. Machine tools will have sensors that will collect many different kinds of data, including data on how much the machine has operated, the conditions it has operated in, and the condition of the components of the tool.
The History of Industry 4.0
If you are in the manufacturing world, you may be aware of the more and more commonly used term “Industry 4.0.” What is Industry 4.0 and what is the history behind it?
The history of Industry 4.0 tracks the manufacturing industry from the industrial revolution to the digital transformation and beyond. Each new stage represents a revolution in the manufacturing process that has changed the way we think about and work in the industry.
Industry 1.0 – The Industrial Revolution
It all began with the first industrial revolution, or what most historians refer to as simply “The Industrial Revolution.” This was when the primary means of manufacturing moved from manpower to machine power.
Fuel sources like steam and coal made machine-use more feasible, and the idea of manufacturing with machines quickly spread. Machines allowed faster and easier production, and they made all kinds of new innovations and technologies possible as well.
Industry 2.0 – The Technological Revolution
The first Industrial Revolution represented the period between the 1760s and around 1840. This is where the second industrial revolution picked up. Historians sometimes refer to this as “The Technological Revolution,” where superior electrical technology allowed even greater production and more sophisticated machines.
Industry 3.0 – The Digital Revolution
Although we usually don’t think of the 1950s as the period in which our world became digital, it was here where the digital revolution began with the first computers. These early computers were often very simple, unwieldy and incredibly large relative to the computing power they were able to provide, but they laid the groundwork for a world today that one is hard-pressed to imagine without computer technology.
Industry 4.0 – The Automation Revolution
So we have arrived at Industry 4.0, a term first coined in Germany at the Hannover Trade Fair in 2011 by Bosch. Industry 4.0 is characterized by the level of automation that we have achieved, where machines can often largely govern themselves, in many ways by using internet technologies, or “the Internet of things.” Other features of Industry 4.0 include the use of cloud technology and the importance of big data.
Machine tools will become a part of this smart system. Industry 4.0 will change them in a range of ways and, through them, change the manufacturing sector. Here’s a look at how.
- Preventative Maintenance
One of the main tenets of Industry 4.0 is data collection. Machine tools will have sensors that will collect many different kinds of data, including data on how much the machine has operated, the conditions it has operated in and the condition of the components of the tool.
By collecting this data, machines could estimate when a component needs replacement. For example, the system would alert operators to replace a bearing that has experienced a heavier load and more frequent use sooner than a less used bearing. This predictive maintenance could keep machines running more efficiently and prevent downtime.
- Improved Utilization
Manufacturing operations do not always use machine tools as efficiently as they could, and idle time is a frequent occurrence. For instance, research has found that machine tools are typically actively cutting metal less than 40 percent of the time and sometimes as little as 25 percent of the time.
It can be difficult, though, to determine why this idle time occurs. Collecting data on things like tool changes, program stops and feed holds make finding these answers more feasible and facilitate a more efficient use of machine tools.
- Energy Savings
Smart machine tools and factories can also collect data on energy use to help save companies money. Internet of Things technology, the tech that connects individual devices via the Internet, is also showing up more often in the energy industry. Smart meters and other innovations help energy to flow more efficiently.
A smart factory could use data on electricity demand to ramp up production when energy demand, and, therefore, the cost of energy, is low. Smart tools could also power down or reduce their power use when it’s not needed.
- Avoiding Improper Use
Industry 4.0 will also help identify when machines are being used improperly. For example, if a machine knows the amount of force or temperature it can withstand as well as how the operator plans to use it, it can send out an alert if it detects conditions outside of that norm. This could help prevent misuse caused by human error or malfunction, which could avoid downtime as well as worker injury.
- Improved Quality Assurance
Manufacturers spend a lot of time and resources on quality assurance, taking care not to let any faulty products slip through. The massive amounts of data that smart machine tools would collect about their use could help them to spot potential quality issues.
If a machine operates in a way that isn’t typical, this will show up in the data. Operators may also even be able to track down any products that the mistake might have affected. The use of automation could also improve quality by reducing the natural variation that comes with human action.
- Change in the Role of Humans
Human workers will not become totally obsolete, but such a drastic change in the manufacturing world will require a change in the roles they play. Many jobs will shift from physically operating machine tools to operating them via computers, monitoring data, and providing oversight to automated operations. This will require some substantial retraining. Companies and workers should start now to avoid a skills mismatch further down the road.
One benefit of industry 4.0 for workers is improved safety. The technology allows workers to stay further away from the machines and reduces the risk of human error when they do work directly with them.
Getting started with IoT, automation and other industry 4.0 technologies can seem intimidating. It is wise to get involved where possible, though, to avoid falling behind the competition.
To make the transition easier, manufacturers can start introducing advanced technologies a little bit at a time. This will be more manageable and more affordable. While starting small, companies should also develop plans for their technology adoption into the future. It’s also important to consider safety and cybersecurity.
Manufacturers should also try to remember the goal they’re reaching for with their technology integration — better information, better decision-making and better results.