Surgical robots are useful for minimally invasive surgery because they can perform precise manipulations of surgical instruments beyond human capabilities in small surgical spaces.
What is a surgical robot?
With the advancement of surgical technology, robots have been combined with AI technology to develop surgical robots capable of assisting in medical operations. Precise, minimally invasive surgeries can be performed with more favorable results by reducing the size of the wound, reducing bleeding, reducing the risk of wound infection, and shortening the recovery time of the patient. Robotic surgery can be classified as supervised control, remote surgery, or shared control. Dexterous robotic arms can perform delicate and tiny operations that are difficult to perform with human hands, or they can assist patients with repetitive tasks. Medical-surgical robots require higher safety and more stability control than industrial robots.
How does a surgical robotic system work?
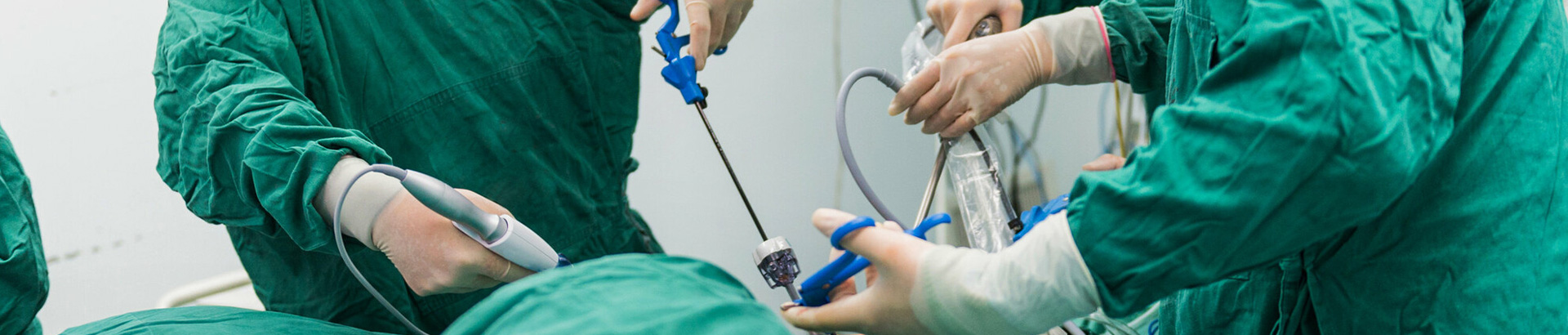
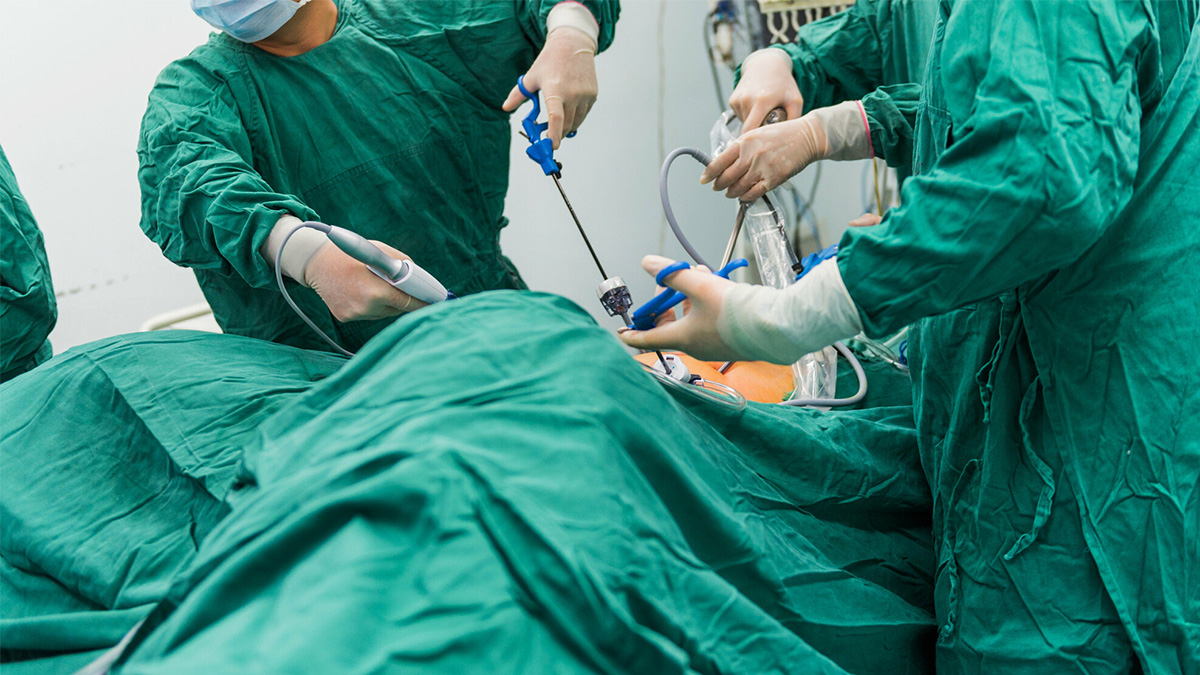
When using a robotic system for surgery, a surgeon makes tiny incisions in your body, inserts tiny instruments and a high-definition 3D camera, and performs the surgery through a robotic arm. During robotic-assisted surgery, the surgeon uses master controls to manipulate instruments that translate the surgeon's movements into precise movements within the patient's body.
A robotic surgery system is a system that allows surgeons to make precise, subtle movements while controlling a machine. Robots do not make decisions or perform surgeries alone. The surgeon gives the instructions and the robot performs the action, with the robot having higher precision than the human hand. Telesurgery robots under the control of a physician provide superior instrumentation and versatile movement through small surgical incisions. Typically, physicians operate ergonomic primary input devices in a visualization environment (physician console), which are translated into motion by a 3D vision system (endoscope) and wrist laparoscopic surgical instruments. The main advantage over traditional (manual) surgical methods is that it compensates for tremors of the human hand and also minimize hand movements for surgical tasks, thereby reducing surgical time.
What are the benefits of robot-assisted surgery?
- Surgeons have a greater range of motion and flexibility
- Surgeons see high-magnification, high-resolution images of the surgical area
- Surgeons have better access to the surgical field
- Shorter hospital stays
- Lower risk of infection
- Less blood loss and fewer blood transfusions
- Reduced pain
- Faster recovery
What surgeries can surgical robots perform?
- Colorectal surgery
- General surgery
- Gynecological surgery
- Heart surgery
- Endometriosis
- Head and neck surgery
- Thoracic surgery
- Urology
Can any doctor perform robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery cannot be performed without proper training. A doctor must be trained in a surgical system to perform surgery in collaboration with a robot.
Predicting Robot-Assisted Surgery Trends:
-
Surgical Robot Market Growth:
The CAGR from 2017 to 2021 was 14.52%. For the surgical robot market forecast, the global surgical robot market is expected to increase from $6.4 billion in 2021 to $14.4 billion in 2026. Driven by advancements in surgical robotics and increased funding for medical robotics research, they are expected to see increased momentum in development.
-
New medical surgery platform:
Hospital budgets across the globe have declined over the past few years, largely due to falling government budgets. Cost cuts have led to layoffs, delays in facility upgrades, and a freeze on capital equipment purchases, such as for high-cost robotic systems. New healthcare technologies are often developed and introduced in response to tight hospital budgets. Given the constant introduction of new, low-cost, powerful enabling technologies such as machine vision, as well as new ownership models, new robotic-assisted surgery solutions will follow.
-
Surgical robots in ASC:
An increase in the use of robotic-assisted technology in ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs) is predicted. ASCs are independent facilities that specialize in surgical, diagnostic, and preventive procedures that do not require hospitalization. The cost-effectiveness of ASC saves governments, third-party payers, and patients substantial money. Robotic-assisted technology can support high-volume, low-cost procedures typically performed by ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs). Robot-assisted technologies reduce operating costs by using standard reusable instruments and open platform architecture, allowing hospitals to leverage existing technology investments, leading to a predictable increase in robot-assisted technology adoption in ASC.
-
Development of telemedicine/telesurgery:
The future of telesurgery depends on 5G technology and robotic assistance. As 5G becomes more common, coupled with advanced robotic-assisted technology, remote surgery will be the way more surgeries will be performed in the future. Existing high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron computed tomography (PET), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) all require the rapid transmission of large amounts of data through 5G technology. In the future, applications such as surgery by a doctor operating a robot remotely through VR will have the opportunity to be realized.
-
Intelligent technology import:
Robot-assisted technology extends to smart healthcare, where big data analysis and application can enhance workflow optimization and achieve new levels of precision and accuracy, ultimately delivering superior surgery.




.jpg)







.png)