The process of milling a plane at right angles to the axis of rotation of the tool.
What is Facing?
Facing is a basic operation that can be done in two ways: Facing on a lathe and facing on a milling machine. Both milling and turning involve the removal of material to produce parts with specific features. Facing is the process of removing material from the ends and/or shoulders of a workpiece, using special tools to create a smooth surface perpendicular to the workpiece's axis of rotation.
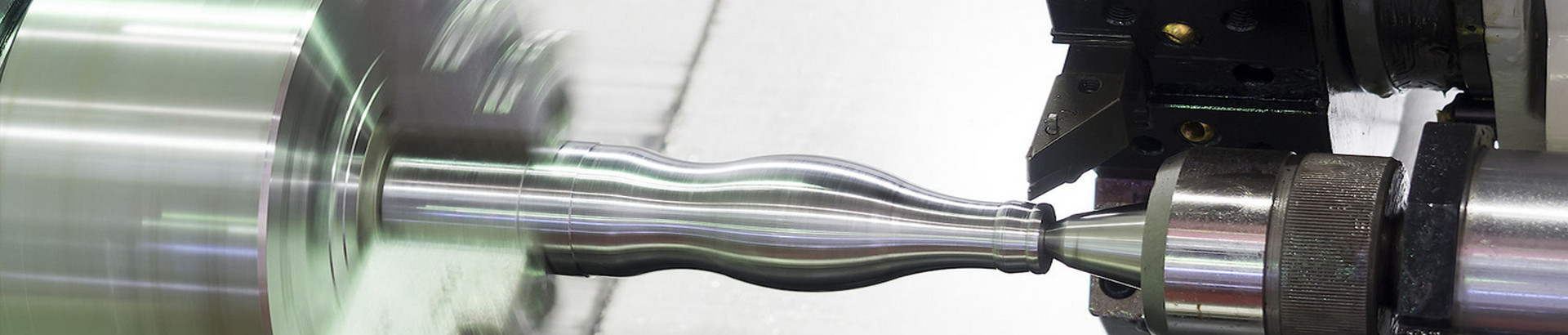
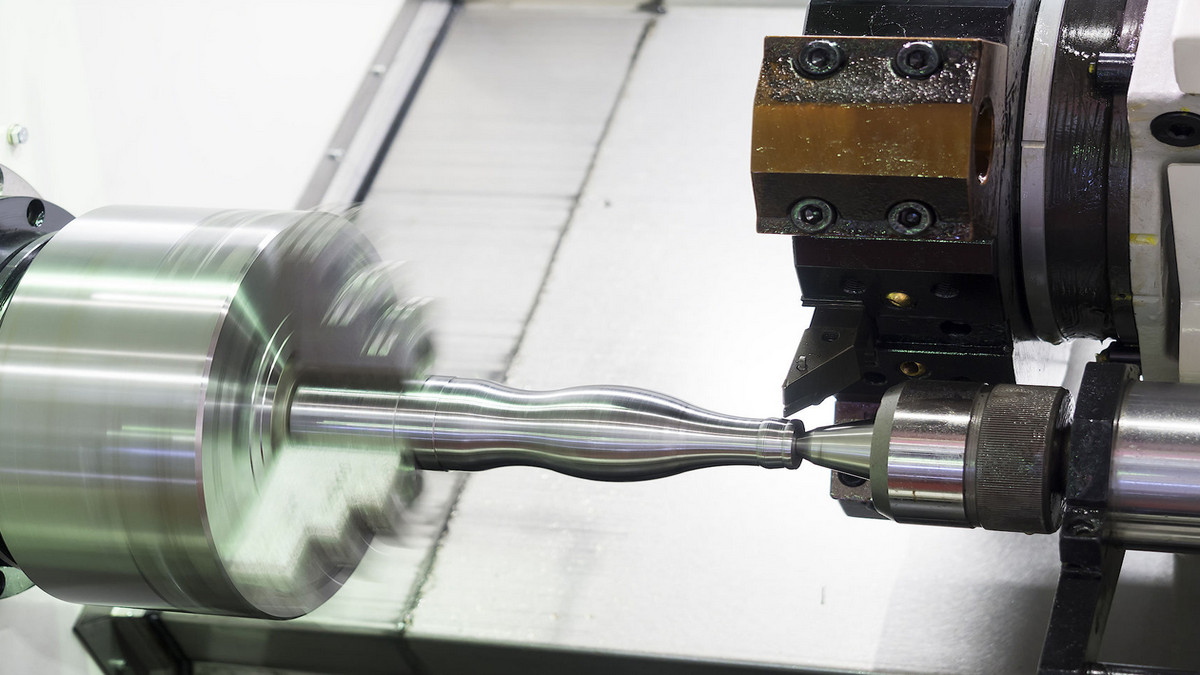
When facing on a lathe, the machinist uses a facing tool to cut a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the workpiece. Then feed the face tool vertically through the shaft. Facing will accurately bring the workpiece down to its finished length, and depending on how much material needs to be removed, the machinist can choose to rough or finish. The lathe face allows the workpiece to rotate relative to the cutting tool.
What is Facing Operation?
Facing is a machining operation that can be performed on a lathe or a milling machine. Facing on the milling machine is primarily face milling while facing on the lathe is commonly used in turning and boring operations. Facing operation is one of the primary ways we can do on the lathe machine when we want to get any shape on a particular part.
Facing on a milling machine removes material by rotating the facing tool counterclockwise while the table feeds the workpiece through the tool. Tools used for face milling include end mills, face mills, shell mills, or fly cutters. Likewise, face milling can be performed manually and CNC machining, providing constant feed for optimum surface finish.
Factors affecting the end face machining performance of lathes:
- Material type of workpiece
- Tool size and material
- Workpiece clamping method
- Spinning speed
In any surface treatment process, it is important to have a qualified surface. Surface qualification is the process of removing microscopic errors on the surface of the workpiece and making the surface as uniform as possible. On the other hand, when facing a milling machine, the live tool moves and rotates around the workpiece. It is not uncommon for milling cutters to have multiple blades or teeth to remove excess material.
For the best surface finish, it is best to let the machine feed the table. CNC machines and newer manual machines have this feature, but older machines often don't. Facing is the basic machining process, but they are the basis for other, more complex machining processes. By quickly creating a large, smooth surface, it is possible to continue other CNC operations and make precision parts to specification.
What is the Operation of a Flat Lathe?
Facing on a lathe uses a facing tool to cut a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the workpiece. The facing tool is mounted in a tool holder located on the lathe carriage. Then, as the tool rotates in the jaws of the chuck, the tool is fed perpendicularly through the part's axis of rotation. Users can choose to manually feed the machine while facing the machine, or use the power feed option. For smoother surfaces, using the power supply option is the best option due to the constant feed rate. The end face will accurately lower the workpiece to its finished length. Depending on how much material needs to be removed, machinists can choose to rough or finish. Factors that affect the quality and effectiveness of face machining on a lathe are speed and feed, material hardness, tool size, and how the part is clamped.
How Does Face Milling Work?
Face machining on a milling machine is the process of cutting a plane perpendicular to the axis of the milling cutter. This process removes material by rotating the face tool counterclockwise as the table feeds the workpiece through the tool. Face milling can be done with an end mill, but is usually done with a face, shell, or fly cutter. Face milling can be done in manual machining and CNC machining. For a smoother surface finish, it's best to let the machine feed the table. Newer manual mills and CNC machines will have this option, but older mills will not. If available, use machine feeding instead of hand feeding the part. This will give the best surface finish as the mill maintains a constant feed. Feeding the table manually introduces human error into the process. Machinists have the option of roughing and finishing. Factors that affect the quality and effectiveness of face milling on a milling machine include speed and feed, material hardness, tool size, and how the part is clamped.
What are the Differences Between Facing, Turning, and Milling Operations?
- The difference between facing, turning, and milling operations is that in facing and turning, the block of material or part to be machined is rotated, while in milling it is a rotating tool.
- Turning tools and face tools are single-point tools, while milling tools are usually multi-point tools.
- In turning operations, the tool generally reduces the diameter of a cylindrical workpiece, which can be done by cutting a certain depth into the part and moving the tool parallel to the axis of the part. Although the face operation reduces the length of the workpiece, the tool moves perpendicular to the axis of the part. In a milling operation, the tool rotates and removes material by moving in a specific direction and angle along the axis of the workpiece.
- Face machining is not limited to workpieces of cylindrical profiles. With the four-jaw chuck, cubes and other non-cylindrical shapes can be formed on rectangular or odd-shaped workpieces.





.jpg)







.png)