Flexible production refers to relying on highly flexible manufacturing equipment mainly based on computer numerical control machine tools to realize multi-variety and small-batch production methods. Committed to the goal of zero switching costs, and reduce this waste as much as possible; then the capacity can be adjusted to make it consistent with the market demand capacity.
One of the important factors in the rise of China's manufacturing industry is the realization of the domestic large-scale production effect, but with the improvement of consumption levels, people are increasingly favoring personalized and customized products. Flexible production is an advanced birth in this context Manufacturing concept. Flexible production will be the direction that some manufacturing companies need to focus on in the future. While flexible manufacturing will transform manufacturing production, it will also have a huge impact on the manufacturing business model.
What Is Flexible Manufacturing?
As mass-production reaches a bottleneck, consumers' personalized needs are increasingly strong. Flexible manufacturing is produced in response to "mass customization" production, which has the characteristics of small batches and many varieties and achieves efficient control of the production process with its good planning.
Flexible manufacturing models are widely available, such as the customization that is common in our lives. This consumer-oriented, production-oriented production mode is the traditional mass production mode. Flexible manufacturing, the test is the reaction speed of the production line and supply chain. For example, the "C2B" and "C2P2B" models that are emerging in the field of e-commerce reflect the essence of flexible manufacturing.
Flexibility can be expressed in two aspects:
- The first aspect refers to the flexible reaction capacity of production capacity, that is, the small-batch production capacity of machinery and equipment.
The device utilization rate and productivity are high, and the unit cost is relatively low. However, it can only process one or a few similar parts, and it is difficult to cope with the production of small and medium batches of many varieties. As the era of mass production gradually moves towards the era of production-oriented to adapt to changes in the market, it is the competitiveness of a manufacturing system to develop multiple varieties, high-quality, and low-cost products in a short time. Flexible manufacturing just meets this point, and its weight in the development of the manufacturing industry is getting heavier and heavier.
- The second aspect refers to the agility and precision of the supply chain.
Flexible manufacturing, the supply chain system responds to individual demand for production and distribution. From the traditional "production-to-sale" to "production-to-sale-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-to-be-to-to-to-to-to-be-to-to-to-to-be", the production order is completely triggered by consumers alone, and its value chain is displayed as "Tai Cai to produce to sell to goods" is a fully targeted activity with clear personal characteristics. In this process, it not only poses major challenges to the production machines but also revolutionizes the traditional supply chain.
The "flexibility" of the manufacturing system can be reflected in:
- Device flexibility-When it is required to produce a series of different types of products, the difficulty of the machine processing different parts with the product changes.
- Process flexibility-the ability to use different materials to manufacture a given part/product type.
- Product flexibility-unique conditions to change the economy and speed of producing a new set of parts or products.
- Work flexibility-the ability to deal with failures, and continue to manufacture a given set of parts/product types, using alternative routes.
- Flexible production capacity-the ability to maintain profitability in different series of production volumes.
- Expansion kit flexibility-The potential of the expansion kit is gradually expanded in a modular manner.
- Production flexibility-the volume of parts/product types that the system can produce.
Flexible Manufacturing Technology
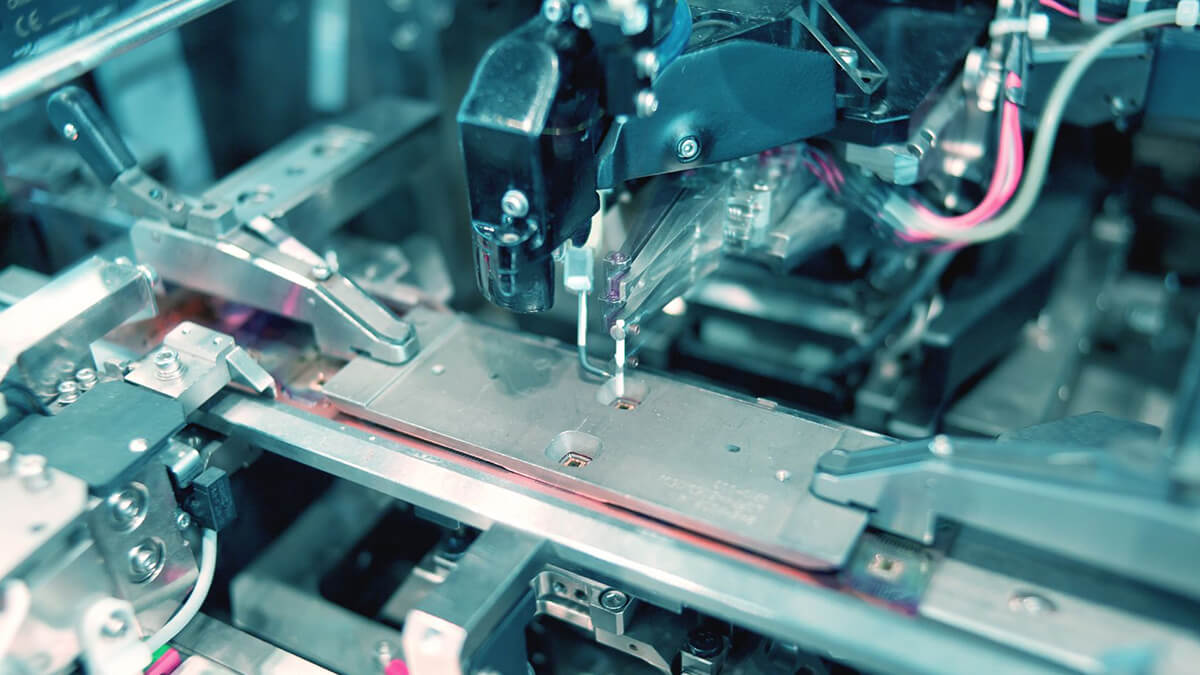
- Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS). Multiple fully automatic CNC machine tools, connected by a centralized control system and material handling system, can realize the processing and management of multiple varieties and small and medium batches without downtime.
- Flexible Manufacturing Cell (FMC). The advent of FMC and its use in production are about 6 to 8 years later than FMS. It is composed of 1 to 2 processing centers, industrial robots, CNC machine tools, and material transport and storage devices. It has the flexibility to adapt to processing many varieties of products.
- Flexible manufacturing line (FML). It is a production line between a single or a small variety of large-volume non-flexible automatic lines and small and medium-sized batches of multiple varieties of FMS. The processing device can be a general-purpose machining center or a CNC machine tool; it can also be a dedicated machine tool or an NC-specific machine tool. The flexibility requirement of the material handling system is lower than that of FMS, but the productivity is higher. It is represented by the flexible manufacturing system in discrete production and the decentralized control system (DCS) in the continuous production process. It is characterized by the flexibility and automation of the production line.
- Flexible Manufacturing Plant (FMF). FMF connects multiple FMSs, is equipped with an automated three-dimensional warehouse, and communicates with a computer system. It uses a complete FMS from ordering, design, processing, assembly, inspection, delivery to delivery. It includes CAD/CAM and puts the computer integrated manufacturing system (CIMS) into practice to realize the flexibility and automation of the production system, thereby achieving the full-scale production management, product processing, and material storage and transportation procedures of the entire plant. FMF is the highest level of automated production, reflecting the world's most advanced automation application technology. It integrates the automation of manufacturing, product development, and operation management as a whole, and is represented by the intelligent manufacturing system (IMS) that controls the material flow of information. It is characterized by the flexibility and automation of factories.
Technology has always been an important factor driving the evolution of the business environment, and the current hottest technology upgrade trend is undoubtedly artificial intelligence. At present, although the artificial intelligence industry itself has entered a stable development period, its empowerment for all walks of life is being carried out more enthusiastically.
In the future, large-volume production and low-cost labor-intensive industries will be relocated in large quantities. Small-volume, customized flexible manufacturing capacity will become the mainstream of China's manufacturing industry. The so-called flexible production refers to the realization of mutual conversion between small batch production and large batch production on the production line based on ensuring product quality. As we often mentioned, mass customization is only an important form of flexible production, not a universal standard.
During the implementation of flexible production, the application of intelligent robots has become an important driving force for achieving the optimal goal of flexible production. The key to "machine substitution" is to achieve software flexibility, automatic programming, and automatic operation. It mainly solves the problem of high labor costs encountered by enterprises during operation. On the other hand, in the application process of robots, it can indeed improve the efficiency of related operations, but it does not necessarily improve the overall efficiency of the enterprise. To make the robot fully play its role, it also needs to integrate production, manpower, and information Simultaneous planning of infrastructure and production line infrastructure construction will integrate robot applications into the overall process of industrial production.
Supply chain collaboration is the foundation of flexible manufacturing. In the process of achieving supply chain collaboration, it is necessary to achieve the consistency and unification of the information in all links of the industry chain. ERP is enterprise resource planning management, MES is a factory-oriented management information system. Most manufacturing enterprises ERP and MES are two sets of systems, the two are independent of each other, and the intelligent management system in the world can realize ERP, MES integration and collaboration, further docking with public big data, real-time analysis and sharing of order data and demand data, to establish a real-time collaborative supply chain.








.png)



