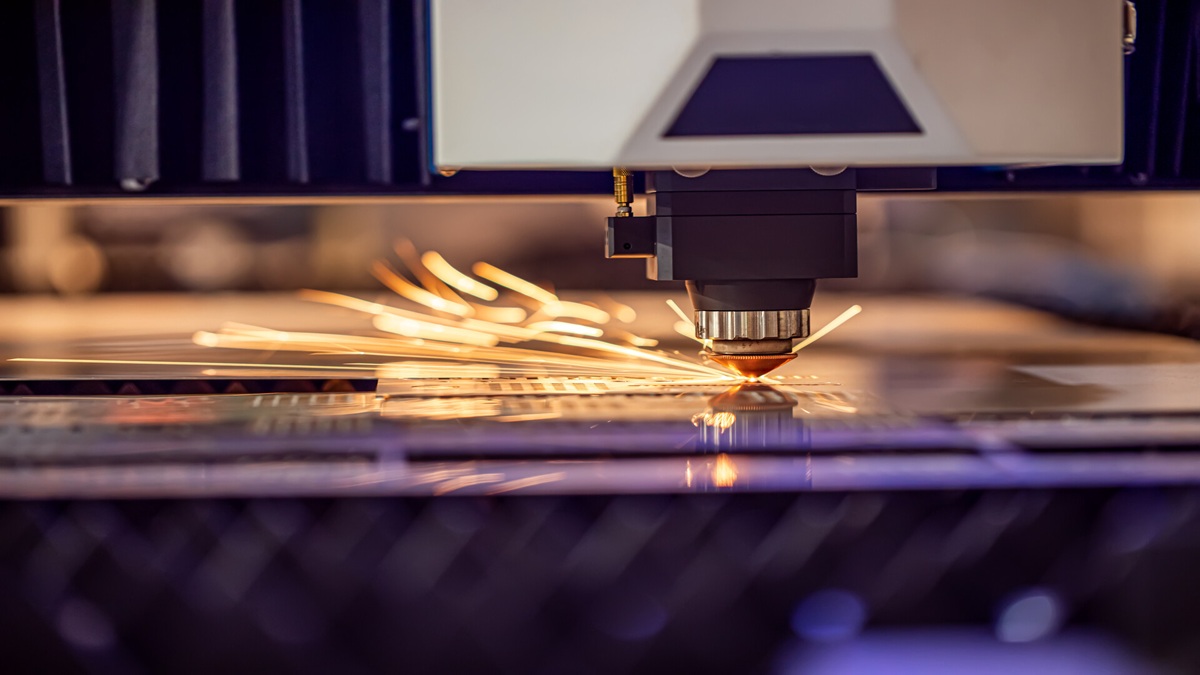
With the rapid development of 3C products and the aerospace components industry, the technology of CNC machine tool rigid tapping is more widely used.
What is Tapping?
Tapping refers to threading the inner wall of a hole and making threads so that corresponding bolts or screws can be connected to it.
Tapping development:
The non-servo spindle control architecture of the early RTEX system was limited by the spindle loop system, and a trade-off between precision and speed had to be made during machining. The machining efficiency was affected and the tool wear was greater, resulting in increased costs. The improvement of the servo control architecture has always been an industry The goal of hard work is to make the CNC machine tool controller provide more precise and high-speed processing characteristics. In recent years, the process of rigid tapping has developed towards the trend of short time, and high precision and the tapping hole diameter and thread must be within standard tolerances.
Internal thread processing is an important procedure in the manufacture of mechanical parts. The cutting method of the traditional floating tapping machine cannot predict the dynamic characteristics of the tap and the material. Under severe cutting conditions, the blade may be worn or broken, and the tool's life will be shortened. The processing conditions affect the manufacturing quality and performance of the workpiece. Rigid tapping is to match the speed and feed with the pitch of the tap and use the synchronous control method to cut the thread with the rotation of the spindle and the movement of the feed axis. This control method improves the pitch accuracy, reduces the damage rate of the internal thread, reduces the problem of tool wear, and improves the service life of the tap, which applies to various cutting materials and cutting conditions. Among them, the path overlap of rigid tapping pecking cycle cutting is high, and the requirements for the synchronous control performance of spindle rotation and servo axis feed are higher. Therefore, rigid tapping synchronous control technology is one of the important performances in the development of machine tool internal thread processing.
Rigid Tapping Synchronous Control Structure:
The control methods widely used in the industry include zero-phase error compensation and cross-coupling control, etc.; the rigid tapping master-slave control structure belongs to tracking motion, that is, the relationship between the main shaft and the servo axis is a straight-line system architecture, and the feedback of the main shaft The position is used as the input signal of the servo axis, and the servo axis with the fast response is used to follow the trajectory of the main shaft. When the movement of the main shaft is disturbed, the error of the main shaft cannot be corrected immediately, resulting in servo lag and tracking error during the movement of the following axis. The tracking error value is theoretically proportional to the speed of the Z axis, so the control system has limitations. The zero-phase error compensation method can enhance the tracking ability of the servo axis and improve the servo tracking error problem, but the disadvantage of zero phase error compensation is the previous feed-forward compensation value is a fixed value. When the processing conditions change or the system is disturbed by the outside world if the control system does not have the ability of adaptive adjustment to reflect the system changes. The feed-forward compensation value must be manually re-adjusted so that the control system maintains motion accuracy. However, manual adjustment is not only time-consuming but also requires experienced processing masters to complete. Therefore, this article will introduce the rigid tapping synchronous control motion architecture. The use of the cross-coupling control method is mainly to improve the servo lag and adjust the position error between the main shaft and the servo axis to reduce the contour error, and greatly improve the rigid tapping processing efficiency and the dimensional accuracy of the thread.
Rigid Tapping Synchronous Control Technology:
The synchronous control of rigid tapping in the controller can be divided into two parts, the control command, and the control loop. When performing G74/G84 rigid tapping, the Z-axis feed corresponding to one revolution of the spindle must comply with the thread pitch specification F/S=P of the tap, so that the spindle rotation and Z-axis linear motion must maintain the same pitch state. The rotation of the main shaft and the Z-axis feed not only have speed control, but position control is more important. The control command must establish a motion control path planning module. In the path planning module, the interpolation amount of the spindle and the Z axis is planned separately. After the motion path is planned according to the spindle speed command and the moving distance of the Z axis, linear interpolation is performed. Make the spindle and Z-axis commands achieve synchronous interpolation control, then the subsequent acceleration/deceleration is also processed independently. And use S Curve to plan the acceleration and deceleration curve to improve the problem of linear acceleration and deceleration jerk, so that the speed curve of the movement changes smoothly. Reduces the vibration of the machine, and reduces the problem of tool interruption during the rigid tapping process.
Variable Gain Cross-coupling Control Law
The variable gain cross-coupling control method in the control loop mainly does not change the motion control loop of each axis but applies the compensator to the control loop of each axis. The purpose is not to improve the tracking error of each axis, but to coordinate the position error of each axis to eliminate the contour error between the two axes, and adjust the contour error according to different trajectory forms. Establish a real-time position error calculation module based on the position response of each axis, and then generate an appropriate feedback signal through the position error compensation module. And distribute it to each axis for compensation, so that the dynamic response of each axis can be matched, thereby improving contour error. The controller in the position error calculation module does not need to modify the motion control structure of each axis, but the position closed-loop control is performed by the error of the position command and position feedback of each axis, and the position error compensation module controls the position of each axis. Adding variable gain CxCy to the loop can moderately adjust the contour error gain value according to different trajectory forms, and then compensate the error value required by each axis to the corresponding axis according to the proportional relationship through the PID control law. This control law Taking into account the mismatch of parameters between the spindle and the servo axis and unstable factors such as incoordination during motion, the rigid tapping synchronous control architecture will use variable gain cross-coupling control to have a good inhibitory effect on the synchronous error of each axis and realize speed control. high precision purposes.







.png)





