The machine tool industry, often called the “mother of industry,” is the backbone of advanced manufacturing across sectors such as automotive, electronics, aerospace, energy, and healthcare. Its value chain spans upstream components, midstream machine tool builders, and downstream application industries, all tightly interlinked. As global market demands evolve rapidly, developments at the downstream level are increasingly shaping upstream technologies and component innovations, creating a dynamic cycle of interaction.
Downstream Demand Analysis
Downstream industries demonstrate increasingly diverse requirements for machine tools. Semiconductors and precision electronics demand ultra-high accuracy and micro-fabrication; aerospace emphasizes rigidity and the machining of large structural components; and the renewable energy sector has become one of the fastest-growing application areas.
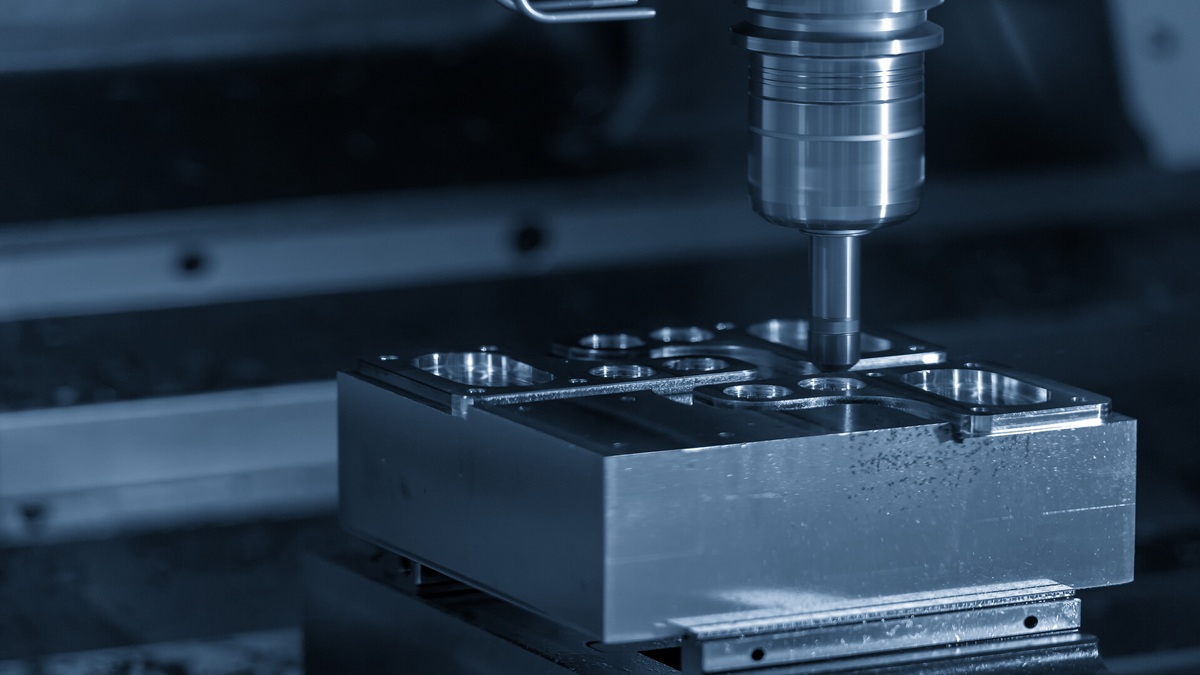
In wind power, the manufacturing of blade molds, spindles, gearboxes, and large bearing housings relies on Largeness Plano Milling Machine , Five-axis Machining Centers, and Turning and Milling Center, where rigidity, machining range, and precision directly determine product quality and system reliability. In electric vehicles, the mass production of motor housings, reduction gears, and battery casings requires machine tools with high-speed spindles, stable cutting performance, and integration into automated production lines.
Beyond these, medical and biotechnology applications demand miniaturization and high reliability, while emerging fields such as robotics and UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) emphasize specialization and multi-functionality. Overall, customer expectations are expanding from traditional machining capability toward precision, efficiency, material adaptability, and intelligence—continuously driving technological advancement in the machine tool sector.
Strategies of Machine Tool Manufacturers
To address diverse markets, machine tool builders are shifting from general-purpose equipment to specialized and multi-tasking machines designed for sector-specific applications. In parallel, the adoption of smart manufacturing, encompassing IoT, AI, and automation solutions is becoming more widespread, enhancing productivity and flexibility. Beyond technological advancement, strategies emphasizing differentiation and value-added features are gaining traction, enabling machine tool manufacturers to sustain competitiveness in an increasingly globalized and competitive market.
Upstream Supplier Responses
Upstream component suppliers play an essential role in the value chain. Core elements such as spindles, bearings, servo systems, and castings must continually advance in precision, durability, and stability to support long-term, high-speed machining. Suppliers are responding by investing in R&D, standardizing production, and collaborating with machine tool builders to co-develop application-specific solutions. At the same time, supply chain integration and risk management capabilities are becoming increasingly important to ensure resilience amid global market fluctuations.
Global Trends & Industry Collaboration
The global machine tool industry is evolving along diverse paths. Europe and Japan continue to lead with high-end precision technologies; North America emphasizes automation and digitalization; while East Asia is advancing smart manufacturing and expanding market scale. These varied approaches highlight that industrial development is not driven by a single model but is instead progressing along multiple fronts. In this context, cross-border collaboration and upstream-downstream co-innovation are increasingly critical. Looking ahead, the industry will depend more on shared technology platforms, international standards, and digital transformation. Policy support—such as R&D incentives, sustainability initiatives, and global cooperation frameworks—will further enhance international connectivity and collaborative growth.
Outlook & Conclusion
Looking ahead, the machine tool industry will continue to be shaped by smart manufacturing, sustainability, and emerging applications. Key growth areas include high-precision five-axis machining, intelligent multi-tasking equipment, and low-carbon energy-efficient technologies. To seize these opportunities, stronger collaboration across the value chain is essential, supported by innovation, digitalization, and market diversification to enhance global competitiveness. Ultimately, the dynamic interplay between downstream demand and upstream technological response remains the core driver of the industry’s evolution and international collaboration.









.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
