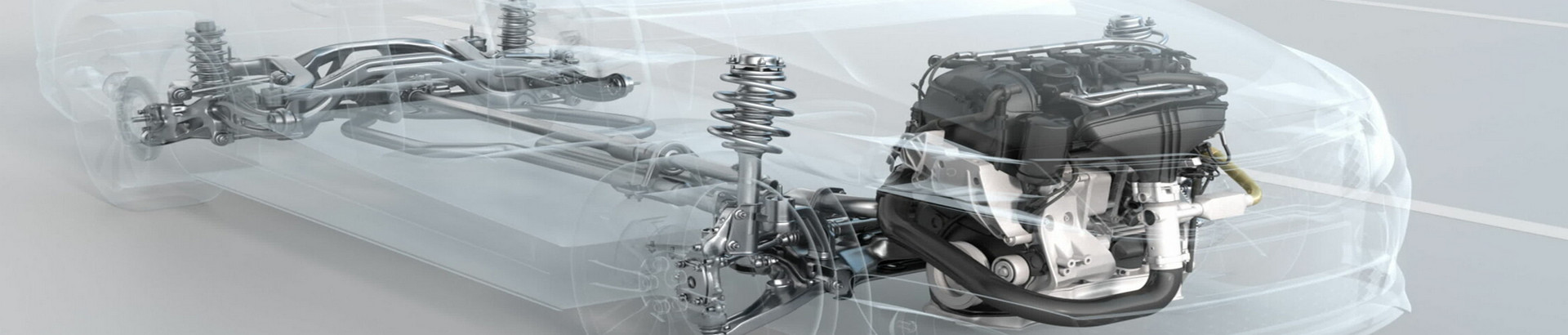
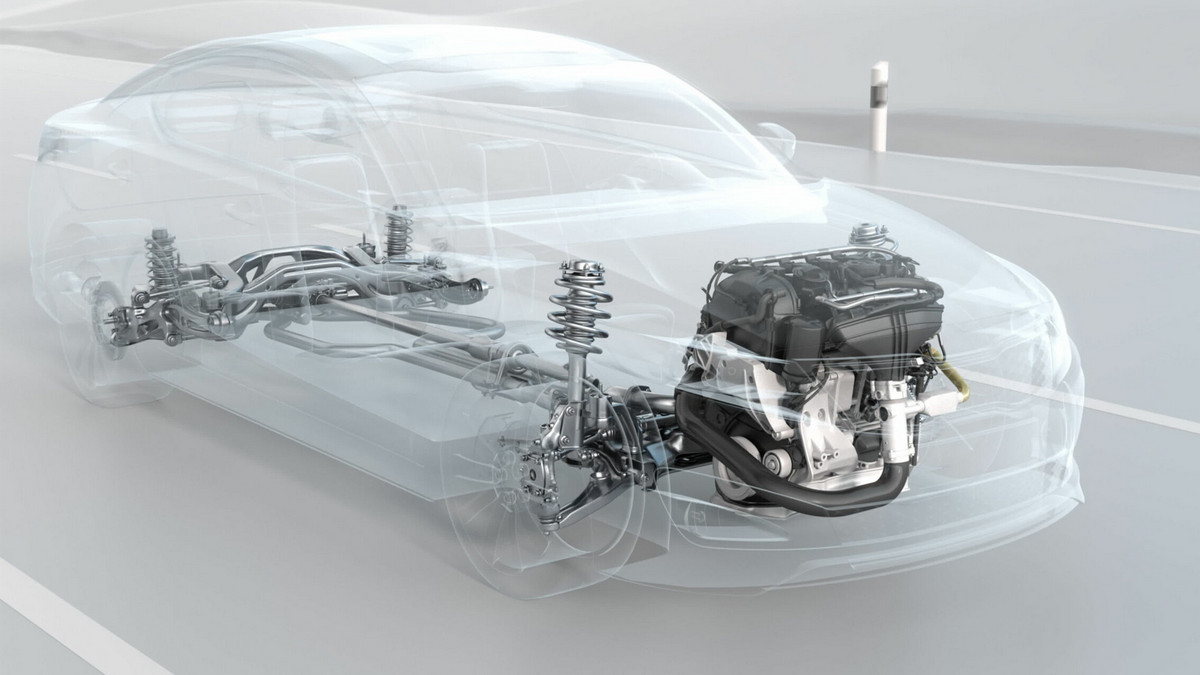
The automobile industry is a technology- and capital-intensive industry, and its industrial chain is quite large, affecting a wide range of related industries. The upstream of the automobile industry is about production of auto parts, such as lights, tires, sheet metal, aluminum alloy steel rims, hoods, bumpers, and others; midstream is vehicle assembly, repair and technical services; downstream is sales, import and export business.
The automobile industry is a technology- and capital-intensive industry, and its industrial chain is quite large, affecting a wide range of related industries. Services and other different industries, and the relevant professionals include R&D, manufacturing, procurement, marketing, management, warranty and other skills, so they are integrated into a complete automotive industry, so the automotive industry is known as the "locomotive industry". The upstream of the automobile industry is mainly related to component manufacturers, the midstream is the large vehicle center manufacturers, assembly, repair and technical services, and the downstream is the brand manufacturers and sales and service bases. Let’s dig in and look at more details at these different stages of the automotive industry chain.
Upstream
Production of auto parts: lights, tires, sheet metal, aluminum alloy steel rims, hoods, bumpers, and others.
There are many processes performed by upstream manufacturers in the automotive industry, including casting, stamping, forging, machining and heat treatment, to produce the many components needed in the completion of an automobile. Due to the complexity of automobile manufacturing and assembly, a single automobile manufacturer may require more than 30,000 parts to produce a single model. Components sourced from upstream suppliers must pass quality inspection before being sent to midstream factories for assembly. Component manufacturers and vehicle assembly factories form long-term and stable cooperative relationships. Each vehicle assembly factory will carry out different degrees of vertical integration with upstream, midstream, and downstream sectors.
Auto parts can be divided into "original car parts" and "after-sales maintenance parts." "Original car parts" can be divided into original factory commissioned equipment manufacturing (OEM) and original factory commissioned design and manufacturing (ODM.) The gross profit of OEM is approximately 10%. For example, Taiwan is mostly OEM, but at present, domestic manufacturers are actively improving their R&D and design capabilities, and are moving towards ODM production for large automakers. This can save mold development costs and provide bargaining power in the supply chain. "After-sales maintenance parts" can be divided into Original Equipment Supplier (OES) and aftermarket (AM) parts. OES parts have the original brand name, but the price is expensive, and the sales channels are mostly designated by the original factory. AM parts are usually used for repair and modification. The products are only copied from existing products, and the price is relatively low. The AM factory mainly produces collision parts, such as sheet metal parts, car lights, plastic parts, cooling parts and so on.
Midstream
Vehicle assembly, repair and technical services.
The midstream of the automobile industry is the central assembly plant. The process of assembling a car in the central plant includes body welding, painting, pre-assembly of some components, and finally the assembly of the whole vehicle. OEMs outsource components to Tier 1 satellite factories, which then subcontract detailed parts to Tier 2 and Tier 3 satellite factories, forming a multi-level division of labor structure. The central factory integrates long-term cooperative upstream component manufacturers and satellite manufacturers. The factory can immediately provide the complete vehicle, parts and technical services required by the downstream sales end, so that the downstream sales industry can reduce the cost related to the self-provided inventory and reduce the operation risk. A complete car must pass various inspection and testing standards under different conditions before leaving the factory. Only after it is confirmed as qualified, can a safe and reliable car be completed.
Electric vehicles will be the new trend of future mobility. The four cores of future mobility are C.A.S.E., Connectivity (Internet of Vehicles), Autonomous (autonomous driving technology), Shared (sharing) and Electrified (electric vehicles). The century-old revolution will also create an unprecedented business model for enterprises. More and more traditional automakers are using strategic alliances to face the huge number of resources, money, and time required for product transformation. Electric vehicles, like mobile phone manufacturing, have entered the era of specialized division of labor, which will create more opportunities for the automotive electronics industry, information and communication industries, and component manufacturers.
Downstream
Sales, import and export business.
The downstream of the automobile industry is vehicle sales and after-sales service. In the first half of 2021, due to the epidemic, the sales of the auto market were not good. However, after the epidemic was under control and the alert was downgraded, a wave of new car purchases was triggered. But due to the global shortage of automotive chips, the industrial chain was in chaos, and production capacity was severely affected into 2022. Auto parts supply chain manufacturers have been quite optimistic going into 2022. With the upsurge of environmental protection and carbon neutrality, the future of electric vehicles is promising, and the future holds many business opportunities for many automakers.
It is estimated that the annual global sales of electric vehicles will reach 27 million units by 2025. The future business opportunities should not be underestimated. At present, major international manufacturers attach importance to the Internet of Vehicles, which has driven the development of automobile intelligence. Through wireless communication technology, vehicle-related information is transmitted to the remote management platform, and the automobile is used as a big data center, integrating navigation, entertainment, information security, and communication. With the rise of the sharing economy, and the rapid development of the Internet of Vehicles, smart cars, smart manufacturing, traffic safety, autonomous driving, and smart transportation, the future of automobiles and components will also move towards mass production and customized services.




.jpg)







.png)