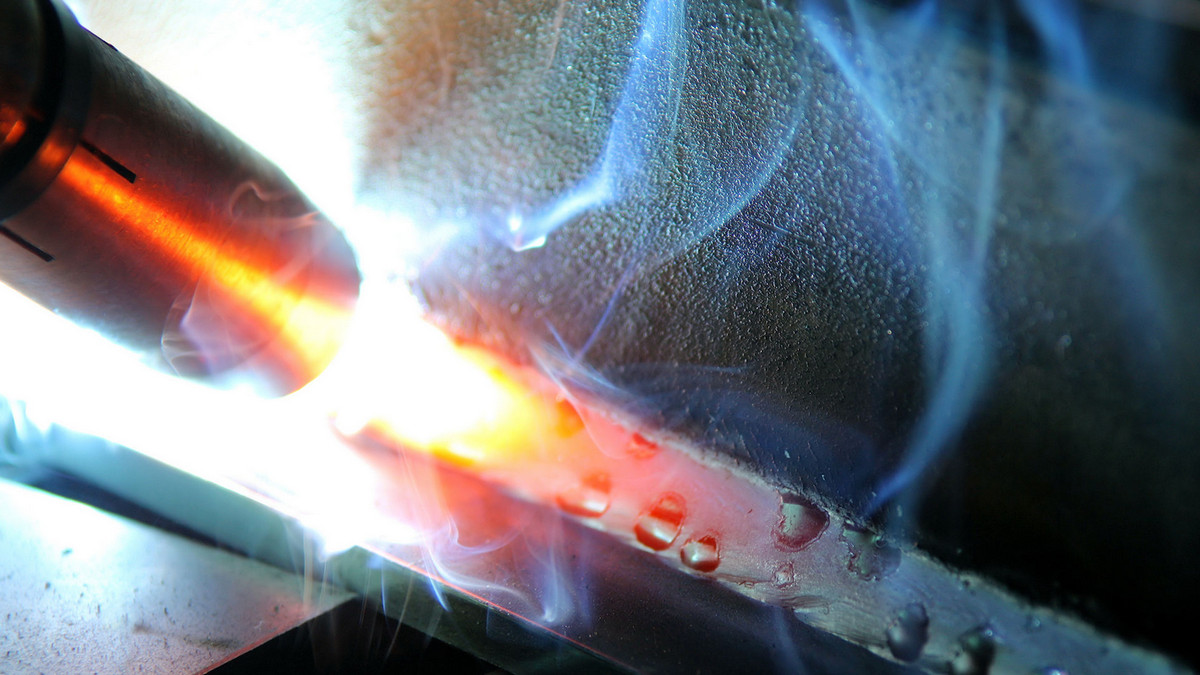
Welding refers to the joining or fusing of workpieces by heating and/or compression to form a continuum. The fusion of weldments can be based entirely on the heat generated by the arc to fuse the weldments.
What is Welding Technology?
Welding is a process and technique for joining metals or other thermoplastics using heat or pressure.
Welding is the process of joining two pieces of metal using heat and electricity. There are many energy sources for welding, including a gas flame, arc, laser, electron beam, friction, and ultrasonic. In addition to being used in factories, welding can be performed in a variety of environments, such as in the field, underwater, and space. Welding can be dangerous to the operator wherever it is, so proper precautions must be taken when welding. The possible injuries caused by welding to the human body include burns, electric shock, visual impairment, inhalation of toxic gases, and excessive ultraviolet radiation.
The seam that is formed to be joined when welding is done is called a weld. Both sides of the weld will be subjected to welding heat during welding, resulting in changes in structure and properties. This area is called the heat-affected zone. Due to the difference in workpiece material, welding material, and welding current during welding, overheating, embrittlement, hardening, or softening may occur in the weld and heat affected zone after welding. Which reduces the performance of the weldment and affects the weldability. Therefore, it is necessary to understand and adjust the welding conditions before welding, including preheating the interface of the weldment before welding, heat preservation during welding, and post-weld heat treatment, which may improve the welding quality of the weldment.
Welding achieves the purpose of joining by:
- The workpieces to be joined are heated to partially melt to form a weld pool. After the molten pool cools and solidifies, it is joined. If necessary, filler metal can be added to assist.
- A solder with a lower melting point is heated separately without melting the workpiece itself, and the workpiece is connected by the capillary action of the solder.
- At a temperature equal to or lower than the melting point of the workpiece, supplemented by high pressure, superimposed extrusion, or vibration, etc., the two workpieces are infiltrated and bonded to each other.
What are the Types of Welding Processes?
According to the specific welding process, welding can be subdivided into gas welding, resistance welding, arc welding, induction welding, laser welding, and other special welding. Among them, the common welding techniques include pressure welding, welding, and gas welding.
- Pressure welding:
Pressure welding is the use of an ultrasonic or extremely high-pressure pressure method to allow two solid objects to achieve atomic bonding to join metal and thermoplastic sheets. Pressure welding is not the welding in our impression that the metal is always treated at a high temperature, to melt it to achieve the bond between the two objects. But the use of high-frequency sound waves and high pressure generates horizontal vibration and pressure on the object. Because the influence range is small and the heating time is short, pressure welding is very suitable for many objects that cannot be melted.
The common feature of different pressure welding methods is that pressure is applied during the welding process without adding other filler materials. Pressure welding methods such as diffusion welding, high-frequency welding, cold pressure welding, etc. are all non-melting processes. After the welding is completed, it does not cause the burning of beneficial alloying elements and the intrusion of harmful elements into the welding like fusion welding, thereby simplifying the entire welding process and improving the safety and hygiene conditions of welding.
- Soldering:
Soldering is referred to as brazing and soldering. The welding method is to use a metal material with a lower melting point than the two workpieces to be welded, and heat the workpiece and this material, the melting point is higher than the object and lower than the two workpieces. After the object melts and solidifies, the workpiece is connected. Hard soldering is a material with a melting point higher than 427°C, and soft soldering is a material with a melting point lower than 427°C. The liquid material is used to wet the workpiece, fill the gap between the two interfaces, and realize the mutual diffusion between atoms with the workpiece by the welding method.
- Fusion welding:
Fusion welding is the most common welding method, that is, the workpiece is heated to a molten state at a high temperature without applying pressure. After melting, the workpiece will solidify and become the state where the two objects we see are connected. Many welding methods are classified as fusion welding, including gas welding, arc welding, ion arc welding, laser welding, etc. In the process of fusion welding, if the air is in direct contact with the high-temperature molten pool, the oxygen in the air will oxidize the metal and synthesize with the alloying elements of the object. If nitrogen and water vapor in the atmosphere enters the molten pool, they will be in the molten pool. In the subsequent cooling process, defects such as pores, slag inclusions, and cracks are formed in the weld, which affects the quality of the weld.
Therefore, to improve the welding quality, gas is usually used to protect arc welding, and argon, carbon dioxide, and other gases are used to isolate other elements in the atmosphere to protect the arc and molten pool rate during welding. When the steel is being welded, adding "iron titanium powder" with a high affinity for oxygen to the coating of the electrode for deoxidation can protect the beneficial elements manganese and silicon in the electrode from being oxidized and entering the molten pool. High-quality weld results can be obtained.
Gas Used for Welding:
In most cases, welding is most often used on steel, but aluminum, copper, and other metals can also be joined using welding techniques, and different types of welding require welders to use different shielding gases, mainly helium. The reason is that the above are inert gases, which can withstand extremely high temperatures without dissociation, and are used to protect and isolate air during welding.
The use of inert gas welding can avoid oxidation of the weld and help ensure that the welded metal is free of other contaminants during the welding process, making the welding result stronger, safer, and a cleaner appearance.
What is a Welding Arc?
The welding arc required in welding is a burst of electrical current created between the electrode and the weldment. An arc occurs when a sufficiently large voltage pulse is created between the weldments. In TIG welding, this can be achieved by triggering the arc or when striking the welding material with the electrode (impact ignition). This is when the voltage discharges like a lightning bolt, causing current to flow across the gap, creating an arc that can reach temperatures of several thousand degrees Celsius, up to 10,000 degrees Celsius. The continuous current from the welding power source to the workpiece is established through the electrode, so the workpiece must be grounded using the grounding cable in the welder before starting welding.
In MIG/MAG welding, an arc is formed when the filler material contacts the surface of the workpiece and creates a short circuit. A highly efficient short-circuit current then melt the end of the filler wire, creating a welding arc. For smooth and durable welds, the welding arc should remain stable. Therefore, in MIG/MAG welding, it is important to ensure that the welding voltage and wire feed speed are suitable for the welding material and its thickness. In addition, the work skills of the welder will also affect the smoothness of the arc, which in turn affects the quality of the weld. The distance between the electrode and the wheel groove and the steady speed of the welding torch is important for successful welding. Evaluating whether the voltage and wire feed speed is correct is one of the important abilities of the welder.
Welding Codes and Standards:
Several international standards and specifications apply to welding procedures and the construction and characteristics of welding machines and supplies. They contain definitions, descriptions, and limitations of welding procedures and welder construction to improve the welding process and welder safety and ensure product quality. For example, the general standard for arc welding machines is IEC 60974-1, while the technical terms for delivery, product form, dimensions, tolerances, and labeling are covered in standard SFS-EN 759.





.jpg)






.png)
