The term MRO is an acronym that stands for maintenance, repair, and operations. The term is used to describe the operations and activities that are associated with the upkeep of a plant or facility and can include the physical maintenance of the structure or building, the systems that operate within the facility, and the equipment used to produce the plant or facility’s primary business output.
What is MRO?
Maintenance, Repair; Operation, or MRO, usually refers to the materials and services that do not directly constitute the actual products being produced in a production process, but are services and products used for maintenance, repair, and operation of equipment used during production.
According to some statistics, the cost of actual materials to produce most industrial electrical end-user products only accounts for about 30% of the total purchase cost, while the cost of planning and developing, business operations, sales and marketing, transportation, after-sales cost, and other costs accounts for 70% of the total purchase cost. The control of hidden costs is a major key for enterprises to improve efficiency and reduce overall costs. MRO procurement is an optimal and effective product circulation mode that integrates the procurement chain and the centralized distribution of all products.
Common types of MRO
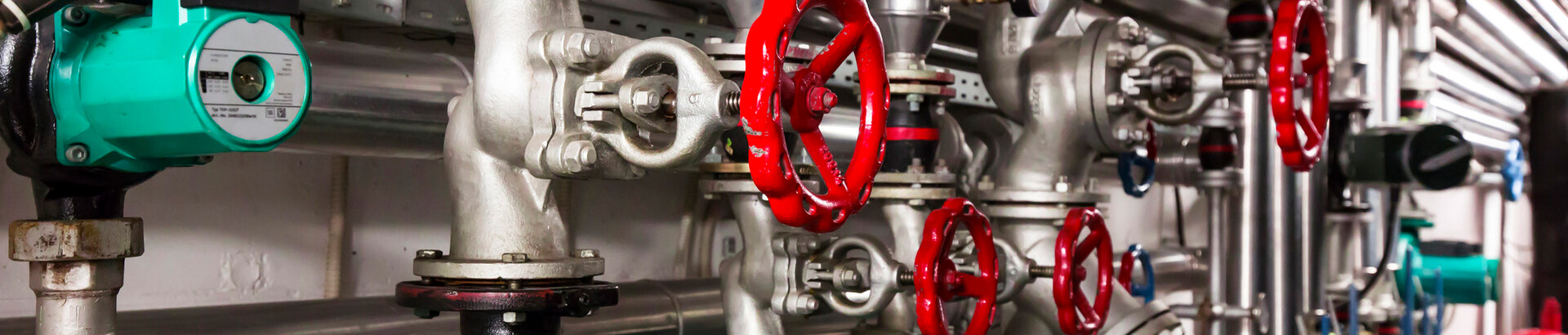
MRO which manages the maintenance and repair of a plant or facility can be subdivided into several areas including:
- Infrastructure repair and maintenance
- Production equipment repair and maintenance
- Material handling equipment maintenance
- Tooling and consumables
MRO materials are usually various types of low-value, consumable commodities with variable purchase volumes, so they are quite different from BOM materials in procurement and inventory management. BOM (Bill of Materials) is a list of the raw materials, sub-assemblies, intermediate assemblies, sub-components, parts, and the quantities of each needed to manufacture an end product. When purchasing MRO materials and managing suppliers, a manufacturers' purchasing personnel can get better prices and services by grasping 5 key points.
Five Things You Have to Know about MRO
Quantity is Strength
Quantity is power, and this is a fundamental principle in negotiations. The buyer's purchasing volume is the buyer's biggest advantage in negotiation, but how to use this advantage reasonably depends on different purchasing strategies. MRO materials usually include a wide variety of low-value items, with low purchase volumes of any single item. If you adopt decentralized procurement, you may be cutting your advantages. If similar goods, or even different kinds of goods, can be combined to purchase, negotiating power is enhanced.
Comprehensive Suppliers
The supplier for a company’s MRO materials may not necessarily be the manufacturer of the materials being purchased, and may not be a large organization. By consolidating procurement projects, sometimes the needs of the buyer can be better met by a small or medium-sized company with comprehensive capabilities. For the manufacturer of a single item, the purchase volume of a single customer may not be very large. Although the manufacturer may have a cost advantage, they may not always offer the best price to the individual buyer. They also rarely reserve a large amount of inventory for individual customers, so the delivery speed is often slower. In contrast, when purchasing through a comprehensive supplier with flexible services, buyers can often get special discounts for large purchase quantities, and they can ask suppliers to reserve a certain amount of inventory, thereby reducing their own inventory to a minimum.
Sourcing Locally
The importance of transportation time and cost in MRO material procurement cannot be underestimated. Since MRO materials are mostly low-value products, if a quarter of a material's lead time is spent on transportation, long-distance transportation will undoubtedly increase the cost of procurement, and sometimes procurement costs may even exceed the value of the material itself.
Use ERP System
The application of a good ERP (Enterprise Resource Management) system can undoubtedly improve the efficiency of an enterprise. For the procurement management of MRO materials, the application of the ERP system can improve the speed of operation, reduce the error rate, and enhance the accuracy of the plan, thereby bringing about a corresponding reduction in procurement costs. But it must be noted that an ERP system is not for everything. For miscellaneous commodities, indiscriminately applying an ERP may be counterproductive.
Timely and Fast Payment
Timely and fast payment is very important for any business. A good supplier relationship is achieved through honest and mutually beneficial cooperation, and timely payment is one of the most important criteria. A good credit record can greatly improve a buyer's position in negotiations, and the buyer will not have a hard time asking the supplier for a longer payment period. At the same time, a good supplier relationship can often enable buyers to obtain supplies at relatively reasonable prices in a timely manner when materials are in short supply, and obtain relatively favorable prices when supplies are abundant. Of course, this depends on the speed of the company's entire payment process and the cooperation of the financial department.









.png)



