There are some differences between the general EDM machine and wire-cut electrical discharge machining. Different processing technologies are applied to different industrial manufacturing needs.
Electrical Discharge Machining, EDM
EDM Machine can be divided into two types: traditional conventional and wire cutting EDM machines. Conventional EDMs use a tool to transfer current from the cathode of the tool along with the sheet metal to the anode, and the current reacts to melt or vaporize the metal. Because the dielectric fluid is used, almost no material debris is generated and washed away from the workpiece.
Wire-Cut EDM
WCEDM is tensioning the thin wire, the subsequent discharge of a live current that acts as a cathode and is guided along the desired cutting path or slit. The dielectric fluid immerses the wire and workpiece in water, filtering and guiding the spark. Fine lines allow for more precise cuts, and the slitting technology can be up to three inches wide and accurately positioned at +/-0.0002 inches. The high precision of the wire-cut EDM allows for complex three-dimensional cutting processes and the manufacture of highly accurate punch dies.
The wire-cut EDM machine is operated by a CNC control instrument that can control the wire on a three-dimensional axis for greater flexibility. Conventional EDM cannot produce narrower angles or more complex patterns, while wire-cut EDM can be performed. A more precise cutting process allows for more complex cuts. The wire EDM machine is capable of cutting a metal thickness of about 0.004 inches. At a certain thickness, the wire EDM wire only evaporates the metal, thereby eliminating potential debris, in addition to all sides of the WCEDM on the wire. Sparks are emitted, which means that the slit must be thicker than the wire itself. On the other hand, since the wire is surrounded by the current loop, the smallest and most accurate cutting path is added to the diameter of the two.
Wire EDM is a metalworking technology and an unconventional process that works on components that are resistant to conventional machining processes, thousands of sparks are discharged onto metal workpieces for cutting, but the necessary conditions are that these parts must be electrically conductive, usually are metal materials such as steel, titanium, alloy, and brass. Instead of cutting the material, the EDM process melts or vaporizes it, producing precise lines and producing less debris, without spending too much workspace. EDM's precision technology is widely used in various industries to cut a variety of hard metals.
Wire Cutting EDM Applications
EDM's technology and functionality, many industrial manufacturing applications in its precision production process, EDM technology can cut small objects, so it is usually applied in small and high-precision complex projects, for small production cost-effectiveness. However, in the production process of EDM, the wires have to be constantly moved and cannot be reused, so copper wires or other metal wires can be several kilometers long, thus increasing the cost. The production process of EDM does not need to be used and avoid cause burrs, so it can be used for fragile items, but the relative attention of thermal stress.
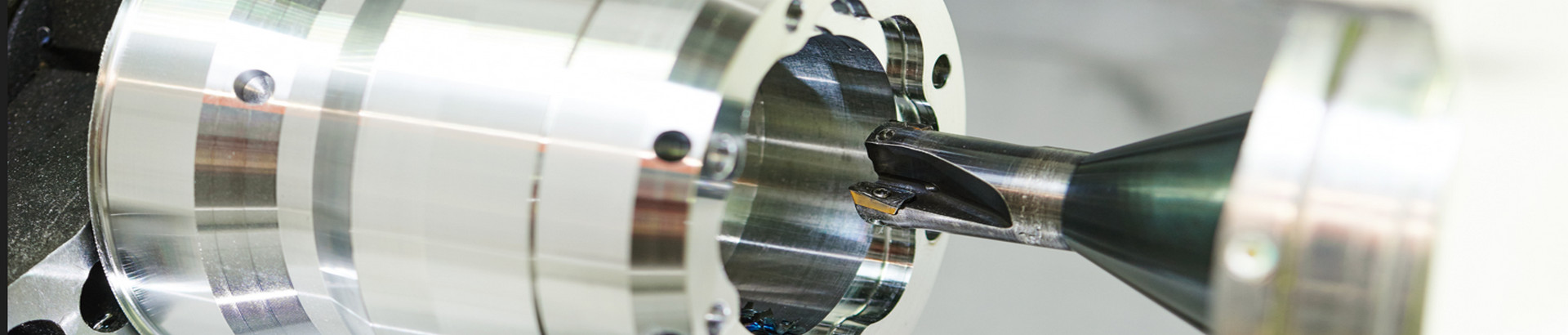









.png)



