Rubber and plastic are both polymer materials, but they differ in origin and characteristics—and their environmental impact after disposal is significant. In response to sustainability challenges, the industry is beginning to optimize processes and materials from the production side, moving toward eco-friendly manufacturing. Taiwan-based Sanhao Rubber has started implementing automation and renewable energy solutions to promote green production and boost competitiveness, demonstrating its dual commitment to both technology and sustainable development.
The Fundamental Differences Between Rubber and Plastic
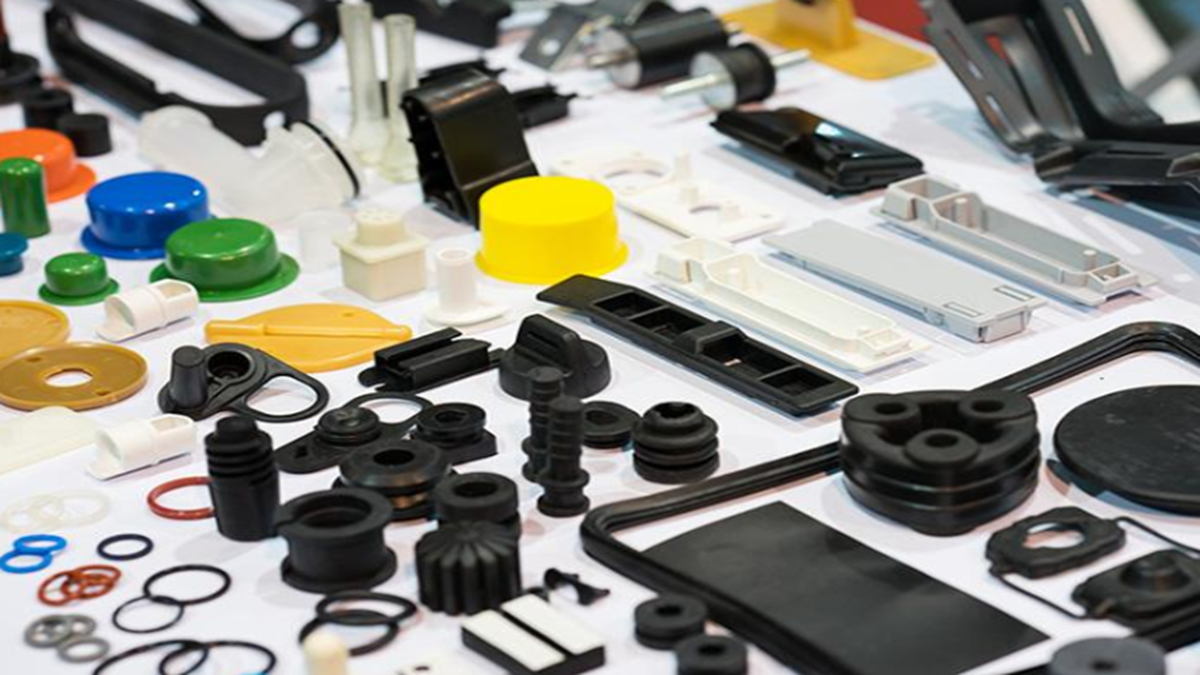
Although rubber and plastic are both polymer materials, they differ significantly in terms of origin and properties. Rubber is primarily derived from the sap of rubber trees and is classified as a natural polymer, while plastic is mostly produced from petrochemical sources, making it a synthetic polymer. Rubber is best known for its excellent elasticity and high tensile strength, making it ideal for shock-absorbing and vibration-dampening applications. In contrast, plastic is valued for its outstanding moldability and formability, making it widely used in the production of packaging, containers, and other molded products.
Irreplaceable Convenience, Unbearable Cost
However, recent studies have shown that incinerating these materials as a means of disposal releases large amounts of toxic gases, posing serious threats to both the environment and human health. On the other hand, if they are buried, rubber and plastic can take hundreds of years to naturally decompose. Without effective waste management solutions, the environmental impact of these polymers continues to grow.
Despite these challenges, plastic and rubber have become deeply integrated into modern life. From medical equipment to transportation systems, many applications remain difficult to replace with alternative materials. This raises an important question: how many of the everyday items we rely on are truly indispensable without rubber or plastic?
Greener Production Practices
In the current landscape of plastic and rubber applications, growing environmental concerns and sustainability pressures are pushing more companies and research institutions to focus on innovations and improvements at the production level. This shift isn't just a response to public calls for plastic and waste reduction—it has also become a key strategy for companies aiming to achieve sustainable development and enhance their competitiveness.
To begin with, there's a noticeable move toward using more eco-friendly, renewable, or bio-based alternative materials, helping reduce dependency on petrochemical resources. At the same time, companies are working to improve material efficiency by refining formulation processes and enhancing production control, aiming to minimize leftover scraps and material waste.
Next, optimizing manufacturing processes plays a crucial role. Many have introduced advanced production technologies and smart management systems to improve yield rates and reduce defects—ultimately lowering energy consumption and resource waste. Some are even adopting circular manufacturing models, reusing by-products or production waste in other steps of the process, moving closer to a “zero waste” goal.
Moreover, a significant amount of R&D is being directed at material innovation and product design. This includes developing plastic and rubber products that are biodegradable, recyclable, or reusable—making it easier to recover and process these items at the end of their life cycle, and thereby reducing their long-term environmental impact.
About Sanhao Rubber
Taiwan-based Sanhao Rubber Co., Ltd. not only possesses solid expertise in rubber manufacturing but also demonstrates forward-thinking in both sustainable operations and smart manufacturing. To boost production efficiency and ensure product consistency, Sanhao Rubber has introduced large-scale robotic arm systems from Germany, significantly streamlining manual processes. These are paired with in-house developed automated inspection systems, enabling full-process quality monitoring and ensuring that every product leaving the factory meets high standards.
Throughout its production workflow, Sanhao continues to refine processes, reduce material waste, and focus on resource reuse—striving for a win-win between production efficiency and environmental responsibility. On the energy front, the factory has installed solar panels on its rooftops, cutting reliance on conventional energy sources and actively fulfilling its commitments to ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles.
Looking ahead, Sanhao is planning to build a fully automated production facility, aiming to enhance capacity, reduce carbon emissions, and lead the way in transforming and upgrading the rubber industry toward a more sustainable future.
Professional Manufacturing, Advancing with Green Responsibility
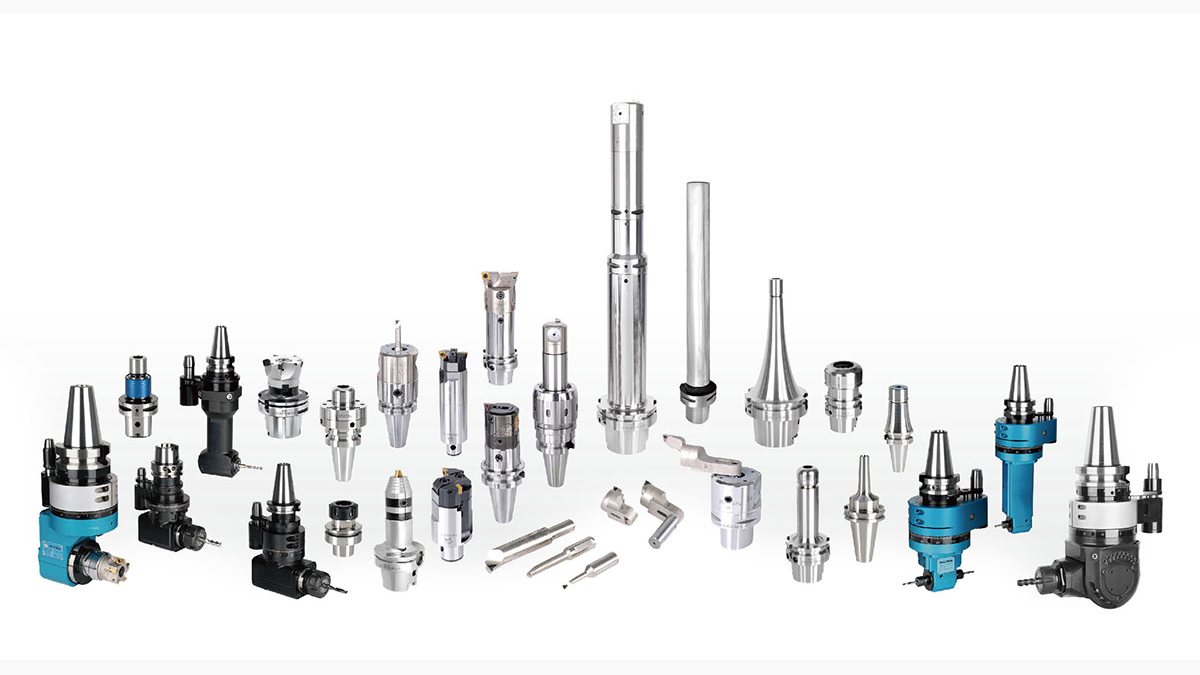
Sanhao Rubber Co., Ltd. has built years of professional experience in both OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturing) and OBM (Own Brand Manufacturing), with particular expertise in handling high-precision, complex CNC lathe components. This reflects the company’s strong technical capabilities and stable manufacturing performance. Whether it’s customized production or large-scale manufacturing, Sanhao consistently delivers on both quality and efficiency—earning the trust of clients at home and abroad.
Notably, Sanhao places equal emphasis on environmental responsibility as it does on product precision and quality. From optimizing manufacturing processes and minimizing raw material waste to adopting energy-saving equipment and using renewable energy sources, the company is committed to reducing its environmental impact throughout production.
For Sanhao, making great products and protecting the planet are not conflicting goals—they go hand in hand as part of the company’s core responsibilities and commitments. With a business strategy that blends technology and sustainability, Sanhao Rubber is steadily expanding its global presence while actively contributing to a greener future.