Advanced manufacturing is the use of innovative technologies to improve products or production processes. Related technologies are called "advanced", "innovative" or "frontier". Advanced manufacturing technology is gradually maturing, integrating innovative technology into products and manufacturing processes to enhance competitiveness and increase value.
Compared with the traditional manufacturing industry, the advanced manufacturing industry refers to the manufacturing industry continuously absorbing high-tech achievements in electronic information, computers, machinery, materials, and modern management technologies, and applying these advanced manufacturing technologies to the research and development of manufacturing products. The whole process of design, manufacturing, online testing, marketing services, and management, to achieve high-quality, efficient, low-consumption, clean and flexible production, that is to achieve information, automation, intelligent, flexible, ecological production, to achieve better Economic benefits and market effects have driven the development and breakthrough of the manufacturing industry.
Advanced Manufacturing Is the Use of Innovative Technologies and Methods to Improve the Competitiveness of Manufacturing
The purpose of advanced manufacturing is to enhance output, increase the added value of products, improve the quality of products, and consolidate the resilience and flexibility to the market. Shorten product R&D and time to market, reduce the unit quantity, material content, material inventory, and capital factories used.
Traditional manufacturing is based on the use of dedicated factories and production lines with little or no flexibility. Advanced manufacturing involves a variety of production methods. These methods can make full use of capital factories, and have higher efficiency, higher efficiency, and faster response speed. Although in some cases, the traditional dedicated method is still applicable (for example, predictable long-term production operation), but advanced manufacturing technology can meet the various production requirements and mass customization commonly encountered in the industry without excessive capital investment.
Advanced manufacturing covers all aspects of the value chain from concept to scrap and relies on information and communication technology (ICT) to integrate manufacturing and business activities into a seamless and efficient operation.
The technologies involved in advanced manufacturing can be divided into three main categories: efficient production, intelligent production, and effective organization.
- Efficient production involves the design, simulation, physical and computer modeling, advanced production technology, and control technology. The point is to do it simultaneously, not sequentially. Related production technologies include rapid prototyping, near-net forming, precision casting, machining, and joining technologies.
- Intelligent production involves the use of ICT in manufacturing and related logistics systems. As well as production-oriented smart machines, batteries, and production lines, this concept involves implementing systems through effective monitoring, maintenance, and repair strategies to extend service life and optimize the use of production facilities.
- Effective organization involves effective coordination and development of manufacturing resources. This includes material resources and knowledge. Related topics include virtual bidding and enterprises, shared facilities and resources, novel organizations, incubation units, knowledge management and transactions, and e-commerce. The focus in this area is to use technology to enhance the participation and capabilities of SMEs and large organizations.
Advanced manufacturing technology can increase productivity in many ways. They enable manufacturers in certain industries to provide customers with the option to "act in their way", thereby greatly increasing flexibility. Manufacturers can also produce products in small batches for specific customers, adjust production lines based on design changes, and even accelerate time to market by quickly generating prototypes.
Advanced manufacturing technology can also promote innovation by allowing manufacturers to create new products that conventional methods cannot produce cost-effectively. They also allow manufacturers to produce high-quality goods that meet the buyer's exact specifications. Moreover, these processes are environmentally friendly because they generally consume less raw materials and produce less waste. By exposing workers to fewer hazardous substances, they also increase safety. According to market observations, the following five technical tools have the greatest potential in the next few years to affect the manufacturing landscape and increase productivity.
-
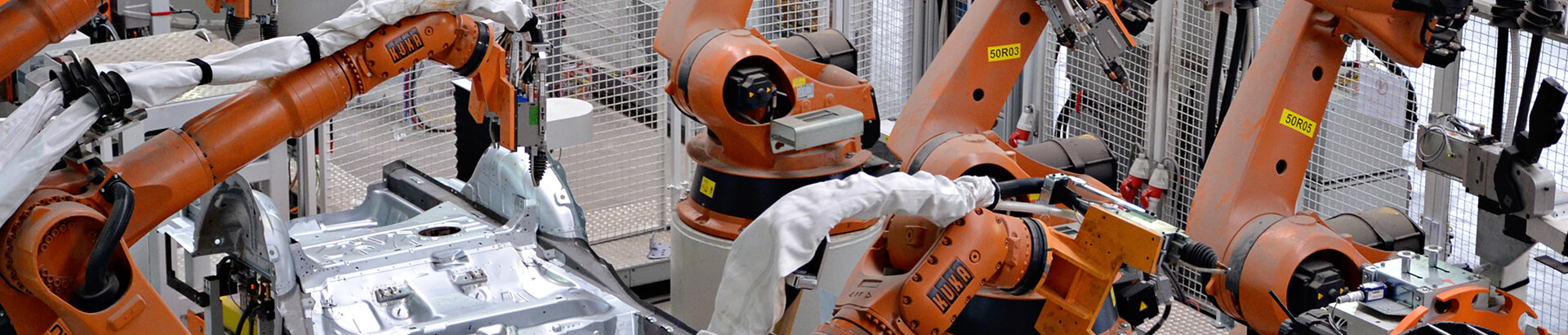
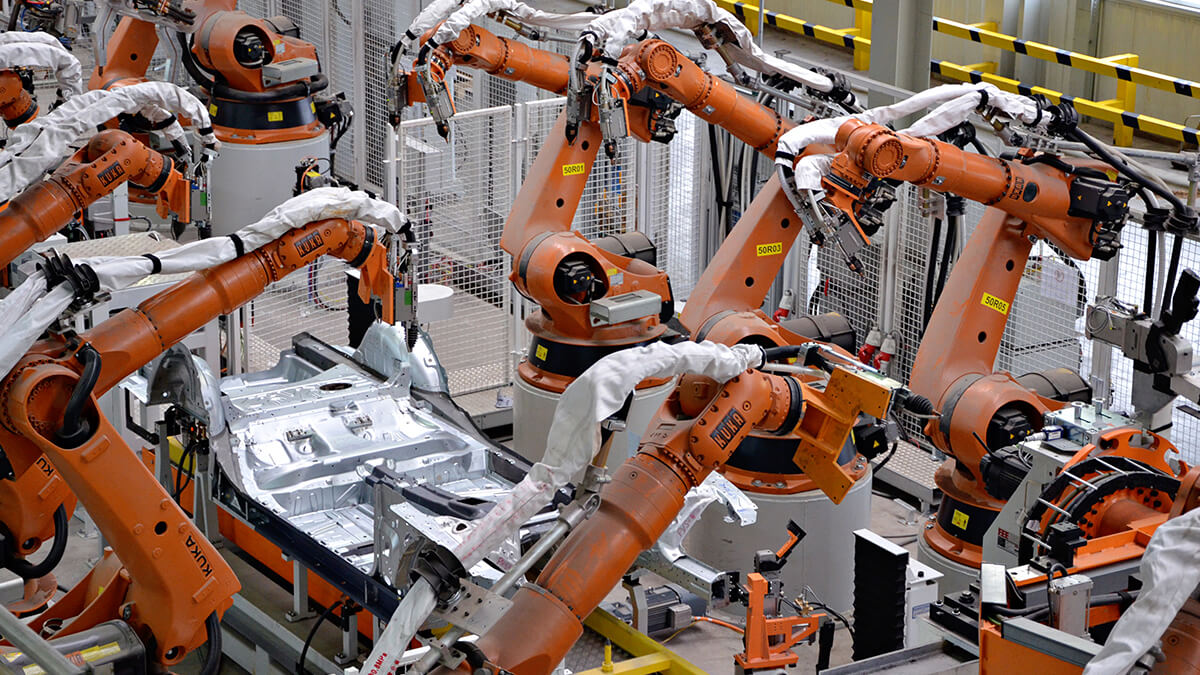
Autonomous robot.
A new generation of automation systems connects industrial robots with control systems through information technology. New robots and automation systems equipped with sensors and standardized interfaces have begun to supplement (and in some cases eliminate) labor in many processes. This allows manufacturers to cost-effectively produce smaller-scale products and improve their ability to improve quality.
-
Integrated Computing Materials Engineering (ICME).
By creating a computer model of a product and simulating its performance before the product is manufactured, instead of building and testing multiple physical prototypes, engineers and designers can develop products better, faster, and cheaper.
-
Digital manufacturing.
Virtualization technology can be used to generate a complete digital factory that simulates the entire production process. Among other things, digital simulation can help engineers save time and money by optimizing factory layout, identifying and automatically correcting defects in each step of the production process, and modeling product quality and output. The entire assembly line can be copied to different locations at a relatively low cost.
-
Industrial Internet and flexible automation.
Manufacturing hardware can be linked together so that machines can communicate with each other and automatically adjust production based on data generated by sensors. They can "see" the supply chain.
-
Additive manufacturing.
The additive manufacturing process is commonly referred to as 3-D printing, which creates three-dimensional objects based on digital models by continuously depositing thin layers of material. Such processes have already been used for prototyping in certain industries, including aerospace, automotive parts, and basic consumer products. In the future, it is expected that these processes will be used to manufacture small batches of a product made of solid material, such as hollow balls without seams.
Five Areas of Work to Consider in Advanced Manufacturing
-
Medical device design and manufacturing- Over time, healthcare is an area that may grow, and the development and manufacture of medical devices contain opportunities.
-
Sustainable manufacturing- In many countries of the world today, as demand grows and consumption increases, we need environmentally conscious solutions and require products to be discarded at the end of their useful lives. Sustainable manufacturing design is very valuable here-if engineers can find products, and even video game methods, these products will eventually become garbage or recycled. Even small appliances need to consider the need to do so.
-
Control sensor development- Develop and utilize embedded sensors to enhance technological breakthroughs in autonomous vehicles and advanced safety.
-
Welding Engineer- Welding engineers are in great demand, and laser and electron beam work are major areas of opportunity. The laser is expanding at a very high speed, and it must also be considered that fusion welding involves electron beams, friction, projection resistance, etc.
-
Supply Chain Strategy- Learning how to qualify a supplier’s products is key, and the final result of the supply chain mechanism ultimately leads to the production of the final product with the correct specifications.










.jpg)


