Reverse engineering is a technical process used to analyze and research a target product. It is used to deduce and obtain the products design elements such as the product's processing flow, organizational structure, functional performance specifications, etc., to produce products with similar functions.
What Is Reverse Engineering?
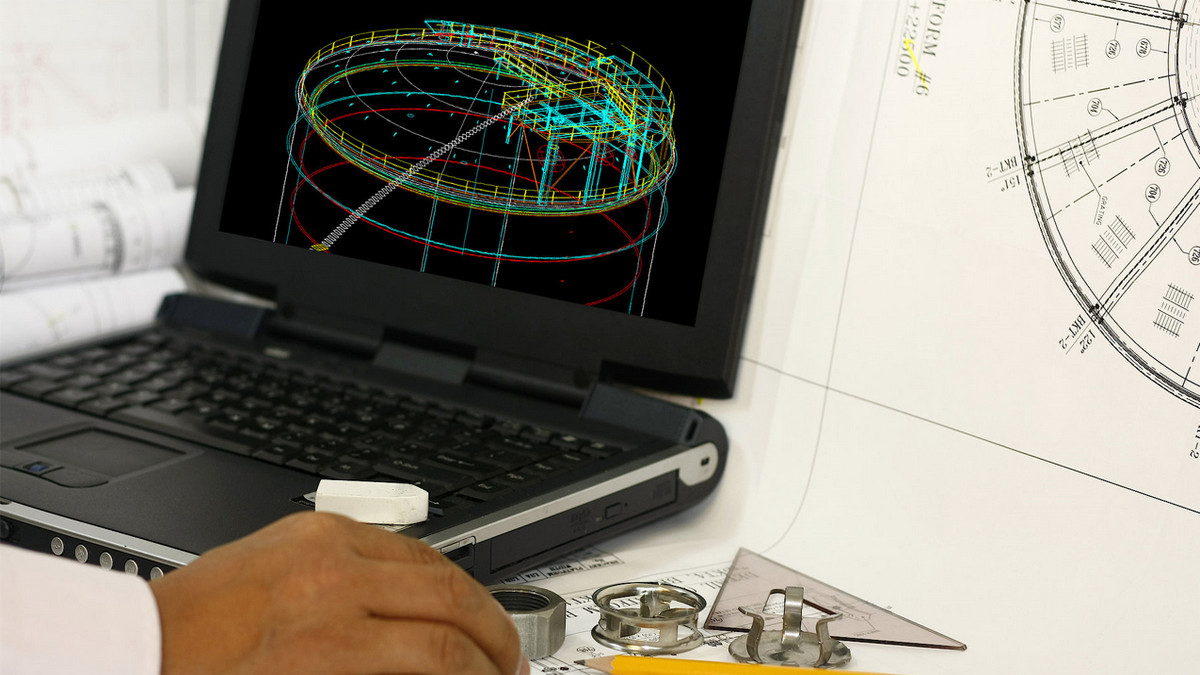
The traditional design process is to create a new product from scratch, and then manufacture it. But what if the original CAD file is lost, or the original CAD data of the part cannot be obtained? Reverse engineering captures the appearance and size information of the finished product through 3D technology (such as 3D scanners, CT scanners, and three-coordinate measuring machines), and then reconstructs the CAD files of the original parts through 3D modeling software.
Reverse Engineering Requires a series of steps to gather precise information about product dimensions. Once collected, the data can be stored in a digital archive. Often, engineers enhance the design with new developments and innovations. Sometimes the design of the original model is completely copied.
Reverse Engineering is used to dissect the finished product to learn its functional material specifications and how to combine them. When a physical or manual model goes through the process of measuring → CAD data creation → 3D printing, or CAM output, it is called reverse engineering. This process can accelerate the timeliness and quality of product development, and can save time and costs.
Phase 1: 3D Scanning Services
After using a 3D Scanner to scan the object, the point data of the object is generated into an electronic file in STL format.
Phase 2: 3D Modeling Services
The scanned point data is used for point, line, and surface reverse 3D modeling to reconstruct the surface data of the object and create an original CAD file (STEP file format).
Why Is Reverse Engineering Necessary?
-
Lost original CAD file:
If the original design file has been lost, damaged, or cannot be restored or opened, the format cannot be modified. In this case, the CAD file (3D scanning + reverse modeling) will be restored through 3D scanning and reverse 3D modeling to quickly obtain digital data.
-
Differences in how products are designed:
In the past, designers may only do 2D graphic design, and then convert the data into 3D through CAD software; but now designers often make a 3D model by hand first, so a reverse engineering tool is required to convert this manual model into a 3D surface model, to facilitate the follow-up work.
-
Analyze competing designs:
When analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of competitors' products, it is usually preferred to use 3D Scanner technology to extract dimensional information and represent this information as a point cloud or automatic real-time mesh to further improve the quality of the products.
-
Accelerate R&D innovation:
Reverse engineering shortens product redesign time, and quickly captures design concepts without the need for manual hand drawings.
-
Product design moves towards freeform surface modeling:
At present, consumers not only consider functionality of products, but consider their appearance as well. However, using the traditional manufacturing method, if the original appearance created by the designer cannot be fully expressed, it may be necessary to use reverse engineering to meet the designer's requirements.
-
To assist manufacturers in rapid production:
Manufacturers can use reverse engineering to quickly produce parts without purchasing expensive parts from OEMs with long lead times.
-
It is not easy to obtain forward design data:
Based on commercial secrets, the original factory does not provide the original CAD data to the downstream manufacturers, but only provides the sample to the manufacturer, so it is necessary to restore the original CAD data through reverse engineering tools.
-
Test positive design results:
Another important function of reverse engineering is the inspection of finished products. This is called CAI (Computer-Aided Inspection.) Generally, quality inspection only tests the finished product. Through reverse engineering tools, a comprehensive quality inspection can be performed on the finished product, which can be evaluated to improve the product’s quality and stability.
-
Preventive Maintenance Program:
Reverse engineering can also be a key strategy in a manufacturer's proactive maintenance program. By reverse-engineering critical components before they fail, manufacturers can stock spare parts and reduce unplanned downtime.
Common Reverse Engineering Applications:
- The original factory terminated the production of goods.
- The files or components provided by the original factory do not conform to the design and need to be remade.
- The original factory no longer exists, but consumers still need the goods.
- The original design has been lost, damaged, and cannot be restored, the data file cannot be opened, or the file format cannot be modified.
- Original design flaws that require improvement, such as thin or thick walls, require a process of digital modification and reproduction.
- To make the designed part last longer, the product must be modified by design.
- Analyze product strengths and weaknesses, or identify new developments through original designs.
- Optimizing design parts so that the designed product can be made new or remanufactured in a cheaper way.
- Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of competitors' products and further improve the quality of their products.
- New product sample development.
- Design of imitation and modification of products.
- Rapid mold making.
- Rapid prototyping.
- Digital inspection of products.
Reverse engineering originated from hardware analysis in the commercial and military fields. Its purpose is to deduce the design principle of the product directly from the analysis of the finished product when the necessary production information cannot be easily obtained.
But on the other hand, reverse engineering may be mistaken for a serious infringement of intellectual property rights. But in practice, it may instead protect intellectual property owners. For example, in the field of integrated circuits, if a company is suspected of infringing intellectual property rights, reverse engineering techniques can be used to find evidence.





.jpg)







.png)