- Showing results for
- 3D Printing
With the growing demand for doujinshi (self-published works), design collections, art portfolios, and brand-related cultural stickers, a new wave of publishing has emerged—making small-batch printing an increasingly vital tool for independent creators in the cultural and creative industries. In contrast to traditional printing’s large-volume requirements and lengthy lead times, today’s creators and consumers are leaning toward printing solutions that are fast, flexible, and highly customizable.
2025-08-08 14:22:11
With over 30 years of experience, Wan Feng Enterprise specializes in sticker and label printing. By combining traditional offset printing with cutting-edge digital technologies, the company has become one of the few in Taiwan capable of handling both variable data printing and cold-chain packaging requirements.
2025-08-07 15:36:08
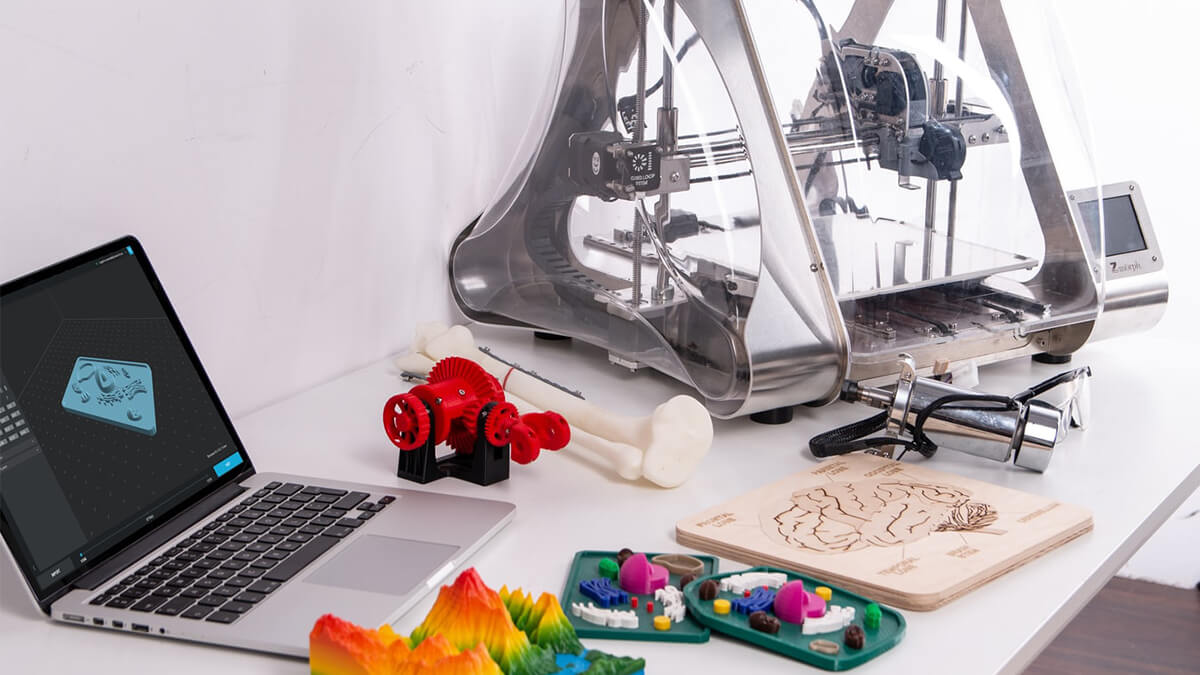
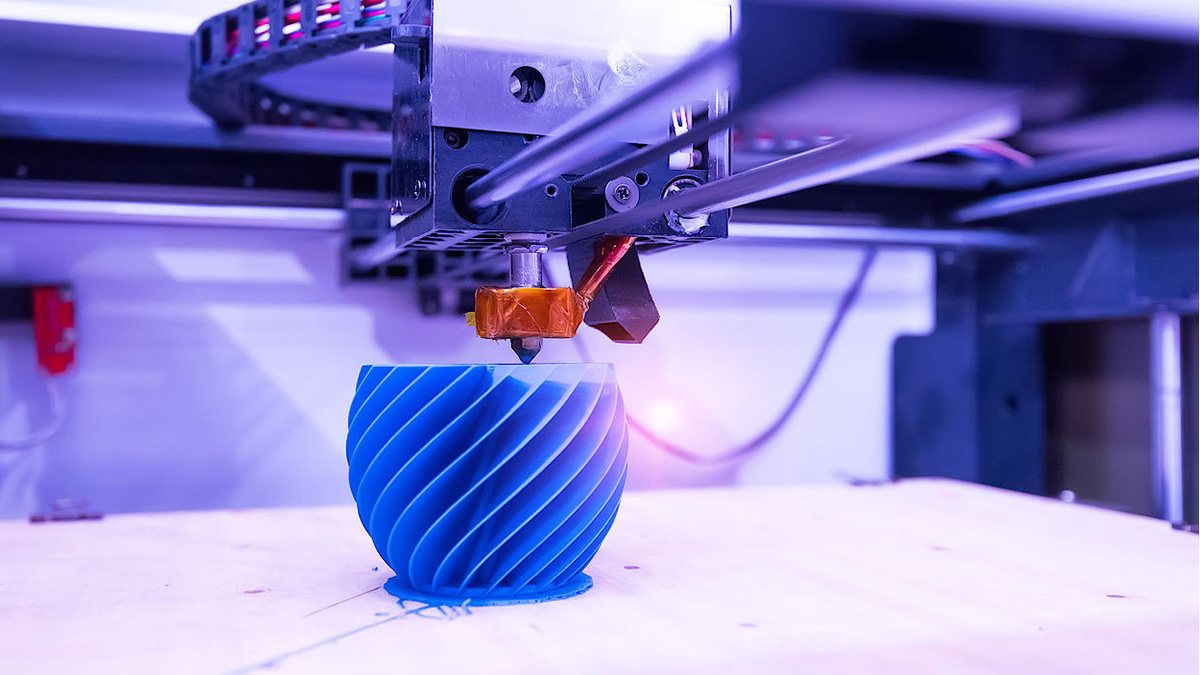
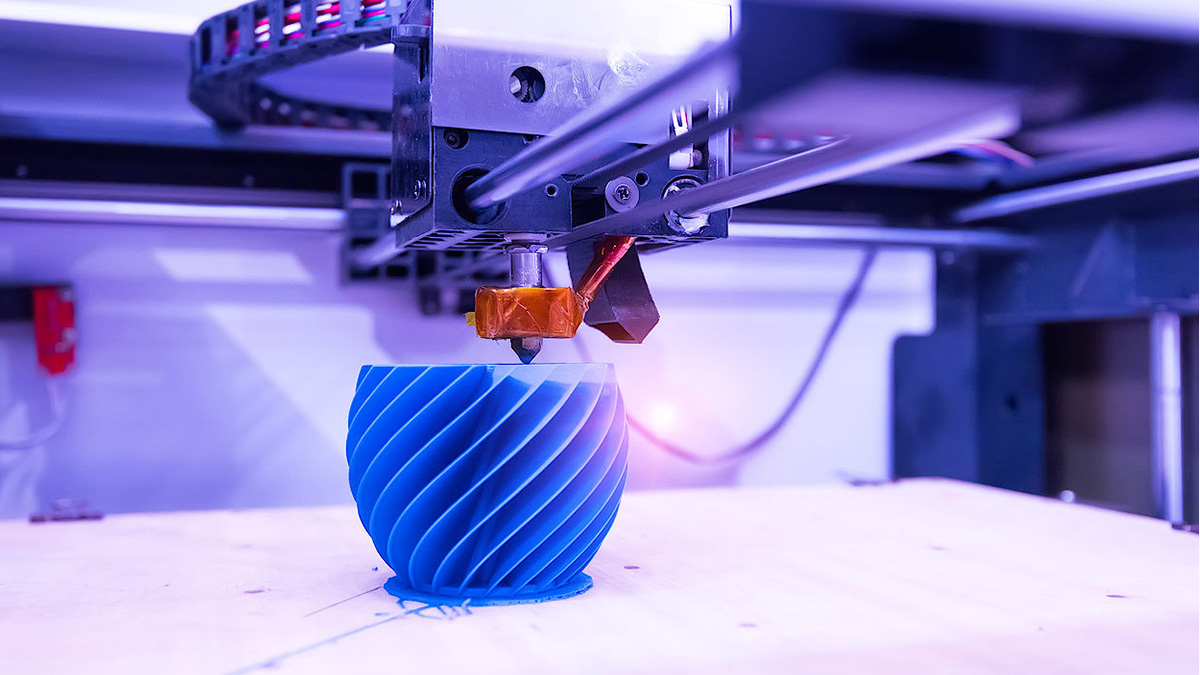
3D printing technology has revolutionized the way industries approach manufacturing, especially when it comes to prototyping. Before its introduction, the process of creating prototypes was often time-consuming, costly, and resource-intensive. Traditional methods involved manual machining or molding, which required significant lead times and extensive human labor. With the arrival of 3D printers, designers and engineers found an efficient solution to rapidly create physical models from digital designs. This innovation allowed for faster iteration and improved communication between teams, ultimately speeding up the development cycle and reducing costs. Over time, 3D printing has not only enhanced prototype creation but has also expanded into full-scale manufacturing, enabling new possibilities for production across various industries.
2025-02-03 14:37:01
As the utilization of 3D printing expands across the broader spectrum of industrial manufacturing, the significance of this technology extends beyond its role as a rapid prototyping tool. This article provides an overview of the applications of 3D printing in the fabrication of molds and dies for processes such as injection molding and die casting.
2023-11-24 14:52:44
The worldwide manufacturing sector is shifting toward smart manufacturing, with Industry 4.0 leading the way by promoting greater efficiency, reduced costs, and intelligent, adaptable production processes. The nine key technologies of Industry 4.0 encompass Big Data, Layered Manufacturing, Cloud Technology, Automation, System Integration, Internet of Things, Cybersecurity, Augmented Reality, and Simulation.
2023-11-03 13:57:30
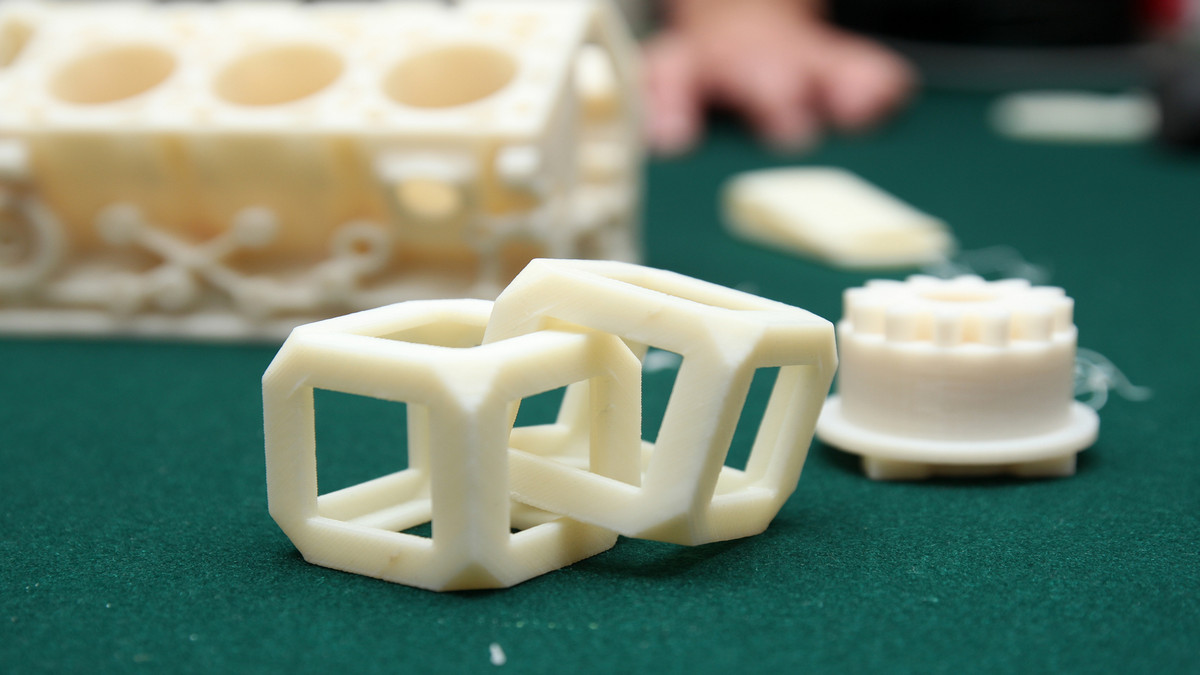
3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing that subverts the thinking of scrap manufacturing in traditional industries.
2023-06-09 13:19:29
As adoption of 3D printing spreads throughout the larger sector of industrial manufacturing, the value of the technology as more than just a rapid prototyping tool is becoming increasingly evident. In this article, we gave an overview of how 3D printing is used to fabricate molds and dies for injection molding and die casting.
2023-05-23 10:46:04
Selective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing technology that sinters small particles of polymer powder into a 3D three-dimensional structure through high-power laser light; thus, this is also called selective laser sintering 3D printing, or SLS 3D printing.
2023-03-16 15:33:33
3D printing technology has been widely used in recent years, and it has also allowed the manufacturing industry to evolve into a "smart" manufacturing industry, which can achieve the large output value with the less manpower.
2023-02-10 09:09:44
With the rapid advancement of science and technology, 3D scan technology has also developed. Through the light source, light with a special structure is projected onto the surface of the object, and digital information is obtained through computer calculation. The versatile 3D scan technology is gaining popularity.
2022-09-05 16:41:07
3D printed end-use parts are going onto vehicles with increasing frequency. Recent real-world examples showcase additive manufacturing benefits in design, weight savings and more.
2022-03-28 15:51:54
The global manufacturing industry is moving towards intelligent manufacturing, and Industry 4.0 is driving the manufacturing industry towards trends of higher efficiency, lower costs, and intelligent and flexible production. The nine technologies of Industry 4.0 include Big Data, Laminated Manufacturing, Cloud Technology, Automation, System Integration, Internet of Things, Cyber Security, Augmented Reality, and Simulation.
2022-01-21 10:42:18
Selective laser sintering is an additive manufacturing technology that sinters small particles of polymer powder into a 3D three-dimensional structure through high-power laser light; thus, this is also called selective laser sintering 3D printing, or SLS 3D printing.
2021-09-09 10:54:53
The printing industry is very complex. It not only has many internal sub-industries but also involves many upstream and downstream related industries. It can be said that it is a huge industry system. The printing industry has a long history of development. Starting from the invention of printing in ancient China, printing technology has continued to innovate, forming a large industry, which we are almost engaged every day. Digital printing, 3D printing, other new emerging printing technologies will overturn and play new roles in printing industry markets.
2021-06-18 13:05:55
3D printing technology has been widely used in recent years, and it has also allowed the manufacturing industry to evolve into a "smart" manufacturing industry, which can achieve the large output value with the less manpower.
2020-07-24 13:54:14
Additive manufacturing has a great future ahead of it. The current development of additive manufacturing has already surpassed the predictions made in studies carried out in previous years. Renowned research institutions such as ETH Zurich are convinced that 3D metal printing will become increasingly important in mechanical engineering and toolmaking.
2020-07-03 13:11:28
Additive manufacturing is playing an increasingly important role in the manufacturing industry and is mainly used in toolmaking and prototype construction.
2020-07-03 11:37:37
In healthcare, 3D bioprinting is used to create living human cells or tissue for use in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
2020-06-04 14:40:18
As adoption of 3D printing spreads throughout the larger sector of industrial manufacturing, the value of the technology as more than just a rapid prototyping tool is becoming increasingly evident. In this article, we gave an overview of how 3D printing is used to fabricate molds and dies for injection molding and die casting.
2020-04-20 09:42:35
The application of 3D printing technology in various industries can lead to new technological breakthroughs and improve production efficiency.
2020-03-24 14:02:20
Agree