Insights
The ASEAN countries' economy is growing stronger, and it is expected to leap into the world's fourth-largest economy in 2030. Taiwan has geographical advantages and is actively developing a south-facing economic island chain.
2020-07-06 17:21:49
In 2019, the global machine tool is facing a severe test, and the market prosperity is not ideal.
2020-07-06 15:04:22
Although the recent impact of the COVID-19 (New Coronary Pneumonia) epidemic caused a short-term loss in the aviation industry, for the overall aviation market, the demand is still constant.
2020-07-06 14:38:57
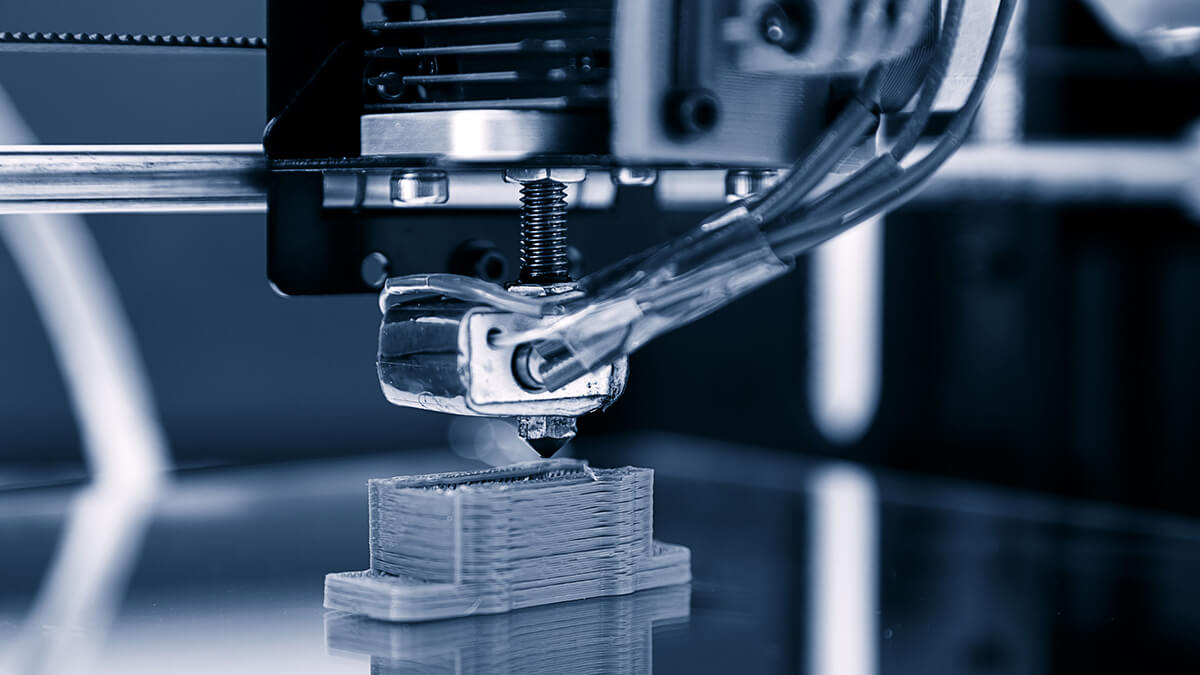
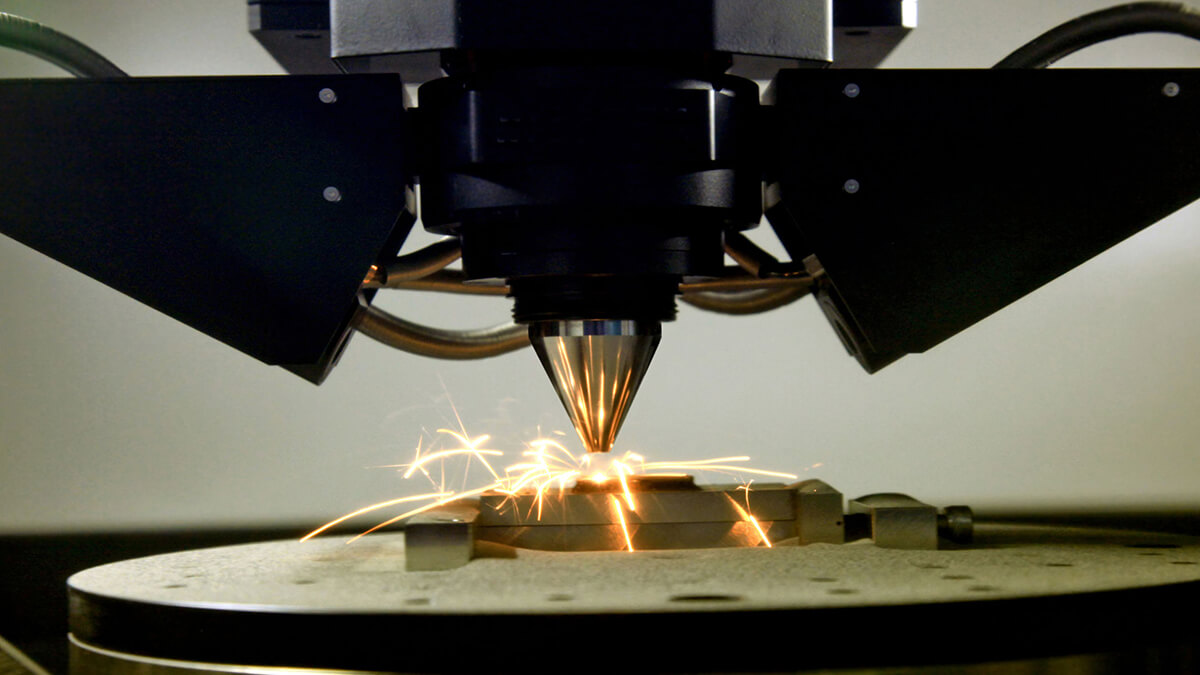
Additive manufacturing has a great future ahead of it. The current development of additive manufacturing has already surpassed the predictions made in studies carried out in previous years. Renowned research institutions such as ETH Zurich are convinced that 3D metal printing will become increasingly important in mechanical engineering and toolmaking.
2020-07-03 13:11:28
Affected by the two major economies of the United States and China, global trade trends have subsided, and the Asian economy has also suffered greatly.
2020-07-03 13:12:52
Additive manufacturing is playing an increasingly important role in the manufacturing industry and is mainly used in toolmaking and prototype construction.
2020-07-03 11:37:37
Advanced manufacturing is the use of innovative technologies to improve products or production processes. Related technologies are called "advanced", "innovative" or "frontier". Advanced manufacturing technology is gradually maturing, integrating innovative technology into products and manufacturing processes to enhance competitiveness and increase value.
2020-06-30 10:28:05
Quenching is a heat treatment process for metals and glass. Heating alloy products or glass to a certain temperature, then rapidly cooling in water, oil, or air containing minerals, generally used to increase the hardness and strength of the alloy.
2020-06-29 15:15:50
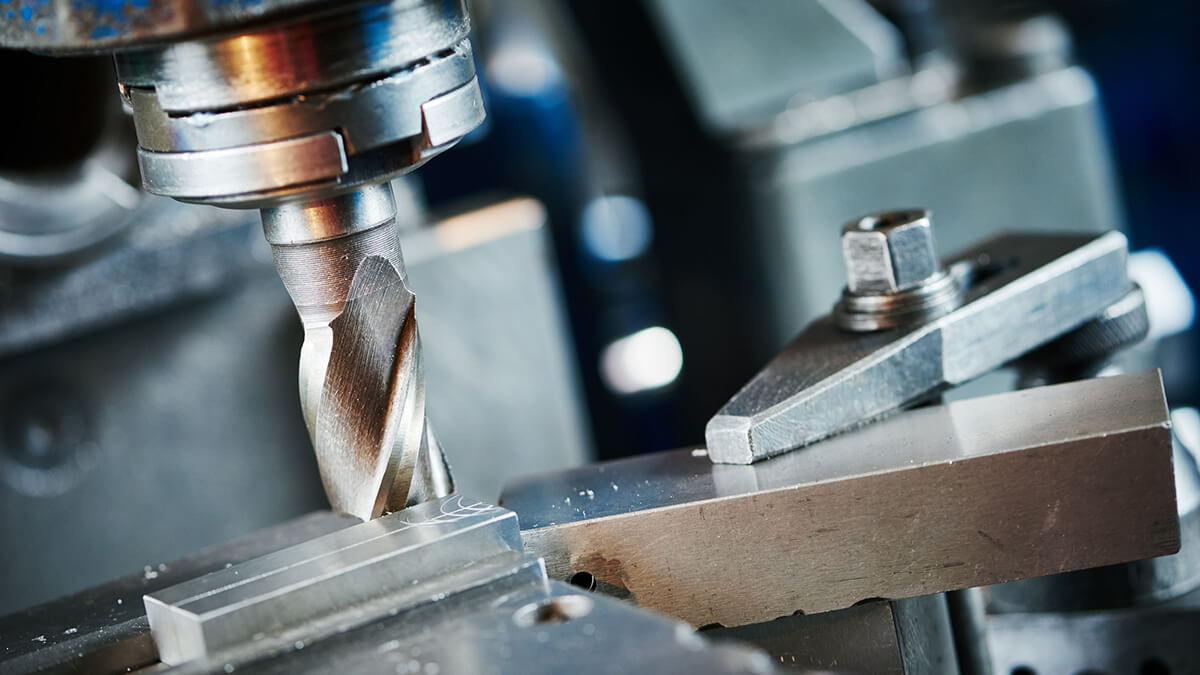
When selecting a milling cutter suitable for the machining task, various issues such as the geometry, size, and work piece material of the parts to be processed must be considered.
2020-06-29 13:23:59
The repair and maintenance of CNC machine tools are very important. Time should be taken in the work to reasonably arrange the inspection work of the machine tools to avoid damage to the work caused by the damage of the machine tools.
2020-06-20 11:07:00
Hot Topic
Agree